What is a Trigger?
Trigger is a procedure in database which automatically invokes whenever a special events in Database occurs. Apex triggers enable you to perform custom actions before or after events to records in Salesforce, such as insertions, updates, or deletions ( Trigger is a piece of code that is executed either before or after a record is updated or inserted.)

What is Trigger Syntax?
trigger TriggerName on ObjectName (trigger_events) {A trigger is a set
of statement which can be executed on the following events. In above trigger
events one or more of below events can be used with comma separated.
· before
insert
· before
update
· before
delete
· after
insert
· after
update
· after
delete
· after
undelete
What are different
type of Triggers?
There are two types
of triggers:
· Before triggers are used to perform a task before a record is inserted or updated or deleted.
· After triggers are used if
we want to use the information set by Salesforce system and to make changes in
the other records. are used to access field values that are set by the
system (such as a record’s Id or LastModifiedDate field), and to
affect changes in other records. The records that fire the after
trigger are read-only.
This type of trigger in Salesforce is used to access the field values set by the system and affect any change in the record. In other words, the after trigger makes changes in the value from the data inserted in some other record.
What are the
considerations while implementing the Triggers?
Consider the
following before implementing the triggers.
· Upsert trigger
fires on 4 different events :- before(insert, update), after (insert, update)
· Merge trigger are
fired on both events on delete
· Field history is
updated after the trigger has successfully finished processing data.
· Any callout should
be asynchronous so that trigger does not have to wait for the response.
· A trigger cannot
have a static keyword in its code.
· If a trigger
completes successfully the changes are committed to the database and if it
fails the transaction is rolled back.
Read the Apex
Developer Guide for more detailed considerations.
What are context
variables in triggers?
All triggers define
implicit variables that allow developers to access run-time context. These
variables are contained in the System.Trigger class.
Following are the
context variable available in triggers. Please note variable availability in
trigger varies according to the type of trigger events.
· isExecuting: Returns true
if the current context for the Apex code is a trigger, not a Visualforce page,
a Web service, or an executeanonymous() API call.
· isInsert: Returns true if this
trigger was fired due to an insert operation, from the Salesforce user
interface, Apex, or the API.
· isUpdate: Returns true if this
trigger was fired due to an update operation, from the Salesforce user
interface, Apex, or the API.
· isDelete: Returns true if this
trigger was fired due to a delete operation, from the Salesforce user
interface, Apex, or the API.
· isBefore: Returns true if this
trigger was fired before any record was saved.
· isAfter: Returns true if this
trigger was fired after all records were saved.
· isUndelete: Returns true if this
trigger was fired after a record is recovered from the Recycle Bin (that is,
after an undelete operation from the Salesforce user interface, Apex, or the
API.)
· new: Returns a
list of the new versions of the sObject records. This sObject list is only
available in insert, update, and undelete triggers, and the records can only be
modified in before triggers.
· newMap: A map of IDs
to the new versions of the sObject records. This map is only available in
before update, after insert, after update, and after undelete triggers.
· old : Returns
a list of the old versions of the sObject records. This sObject list is
only available in update and delete triggers.
· oldMap: A map of IDs
to the old versions of the sObject records. This map is only available
in update and delete triggers.
· size: The total
number of records in a trigger invocation, both old and new.
How is Trigger.New Different from Trigger.newMap?
Trigger.New
variable returns the list of sObject which has invoked the trigger and
Trigger.NewMap returns the map of ID’s with the newly entered records. NewMap
is only available in after insert, before and after the update and after
undelete.
How is Trigger.new
different from Trigger.old?
Trigger.New
variable returns the list of sObject which has invoked the trigger and
Trigger.old returns a list of the older versions of the records which have invoked
the trigger. Trigger.Old is only available in update and delete events
Can a trigger call
a batch class?
Yes, we can call a
batch class in the trigger as we do in the normal apex code.
Can a trigger make
a call to Apex callout method?
we can call a callout
method in Apex Trigger but the only condition is that it has to be an
asynchronous callout because the trigger flow cannot wait on the response
received by the callout method.
------------
Salesforce Workflow:
· It is an automated
process that can shoot an action that is based on evaluation and rule criteria.
· Performing DML
operations in the workflow is not possible.
· You can obtain a
workflow over an object.
· You can’t create a
query from the database.
Salesforce Trigger:
· It is a piece of
code that is executed either before or after a record is updated or inserted.
· More than 15 DML
operations can be used in a single trigger.
· More than 20 SOQLs
can be used from the database in a trigger.
You can access triggers across an object and related to that object.
Salesforce Trigger Example
before insert trigger salesforce
Account trigger to set account rating as ‘Hot’ if account industry is ‘Banking’ or ‘Healthcare’
before update trigger salesforce
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | trigger AccountCustomTrigger on Account (before insert, before update) { for(Account acc : Trigger.New) { if(acc.Industry != null && (acc.Industry == 'Banking' || acc.Industry == 'Healthcare')){ acc.Rating = 'Hot'; } }} |
Please note that in the above example we are not manually updating accounts using DML statement as it is before insert or before update trigger.
after insert trigger salesforce
Let us see one more example of a trigger on contact which will create Account record whenever contact is created without an account.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | trigger ContactCustomTriggerExample on Contact (after insert) { List<Account> accListToInsert = new List<Account>(); for(Contact con : Trigger.New) { //check if account is null on contact if(con.AccountId == null ) { Account acc = new Account(); //Add all required field on Account acc.Name = con.LastName; acc.Phone = con.Phone; accListToInsert.add(acc); } } if(!accListToInsert.isEmpty()){ insert accListToInsert; }} |
Define Recursive
Trigger and how to avoid it?
A recursive trigger occurs when a trigger execution leads to the triggering of the same trigger again, which creates an infinite loop. To avoid
this scenario we should create a static variable and check the value of this
variable before execute anything in the trigger.
to avoid recursive trigger in salesforce use static variables or flags to track the trigger execution and prevent retriggering
Recursion occurs when same code is executed again and again. It can lead to infinite loop and which can result to governor limit sometime. Sometime it can also result in unexpected output.
It is very common to have recursion in trigger which can result to unexpected output or some error. So we should write code in such a way that it does not result to recursion. But sometime we are left with no choice.
For example, we may come across a situation where in a trigger we update a field which in result invoke a workflow. Workflow contains one field update on same object. So trigger will be executed two times. It can lead us to unexpected output.
Another example is our trigger fires on after update and it updates some related object and there is one more trigger on related object which updates child object. So it can result too infinite loop.
To avoid these kind of situation we can use public class static variable.
In RecursiveTriggerHandler class, we have a static variable which is set to true by default.
1 2 3 | public class RecursiveTriggerHandler{ public static Boolean isFirstTime = true;} |
In following trigger, we are checking if static variable is true only then trigger runs. Also we are setting static variable to false when trigger runs for first time. So if trigger will try to run second time in same request then it will not run.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | trigger SampleTrigger on Contact (after update){ Set<String> accIdSet = new Set<String>(); if(RecursiveTriggerHandler.isFirstTime){ RecursiveTriggerHandler.isFirstTime = false; for(Contact conObj : Trigger.New){ if(conObj.name != 'SFDC'){ accIdSet.add(conObj.accountId); } } // Use accIdSet in some way }} |
What do you mean by the bulkifying trigger?
A trigger should be
able to handle single record and thousands of record. There are two important
point for it:
· Write triggers that
operate on collections of sObjects.
· Write triggers that
perform efficient SOQL and DML operations.
If we will not
follow above point we may hit governor limit when records are
created/updated/deleted in mass using data loader or other tool.
Is there any limit on number of triggers define on an object?
We can define as
many triggers on an object as we want but it is recommended to have one
trigger per object because the order of execution of different trigger
is not guaranteed and any trigger can fire first.
Can you explain the
order of execution in Triggers?
Following is the
order of execution of events that Salesforce performs before a DML Event.
1. The record is
loaded from the database or is initialized in case of upset statement.
2. New record’s field
values are overwriting the old values, now depending on the origin of the
request this flow varies: if the request is from a UI page then the following
validations are performed by Salesforce:
1. Any layout specific
rules are checked
2. All the required
values are checked at layout and field level
3. All the field
formats are validated along with the maximum length of field values
If the request
originates other than UI then Salesforce only checks for Validation of foreign
keys.
3. Now all the before
triggers are executed at the database.
4. Most of the
validations are performed again to verify that all the required fields are
holding some values and are not null, at this step user defined validations are
also executed and the only validation which is not repeated in this step are
the rules specific to the layout.
5. After the success
of the previous step, the record is reviewed for duplicate records, by running
the duplicate rule. If a duplicate is found the flow is stopped and no further
actions performed.
6. In this step,
record is saved to the database but it not committed yet.
7. Now all the after
Triggers are executed.
8. In this step,
assignment rules are executed.
9. Now if there is any
auto-response rule is present then they are executed.
10. Next in the queues
are the workflow, they are executed after the auto response.
11. If the workflow was
updating a field, then the fields updated in this step and the flow after this
step varies if this was the case.
12. If a field was
updated then the before and after update triggers are fired once more and
standard validation are also executed again. Custom validation escalation rule
and duplicate rules are not required to run again.
13. Once the execution
has reached this stage, then process is fired if there are any declared on the
object.
14. Now the escalation
rules are executed.
15. Entitlement rules
are executed if any.
16. If there are any
roll-up summary field, then they are calculated at this step and the parent
object go through the save process.
17. Now the sharing
rules are executed.
18. If we reach this
stage, then that means no error has occurred and the data is ready to be
committed to the database and is committed now.
19. Now if there is any
post-commit logic like email, then that is executed.
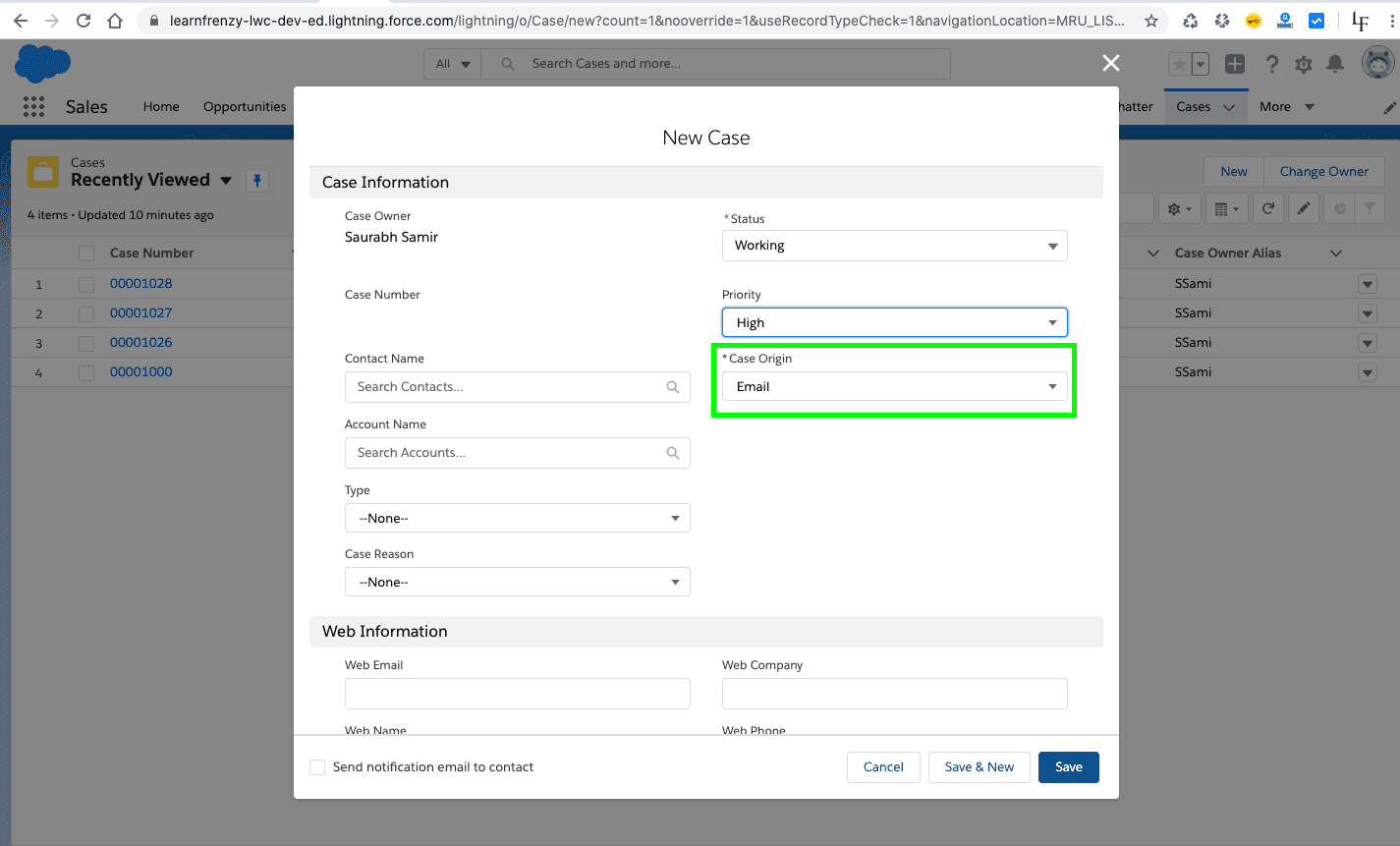
Trigger Scenario 1 :
When ever a case is created with origin as email then set status as new and Priority as Medium.
Object : Case
Trigger: Before Insert
Trigger Code: CaseOrigin.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | trigger CaseOrigin on Case (before insert) { for(case c : trigger.new){ if(c.origin == 'Email'){ c.status = 'New'; c.priority = 'Medium'; } } } |
Output :
–> Case is created with origin as email :
Status : Working
Priority : High
Case Origin : Email
–> Before Insert :
As per the requirement, we are performing an operation on the trigger when the user save the new case that means we need to use as before insert trigger.
Status : New
Priority : Medium
Case Origin : Email
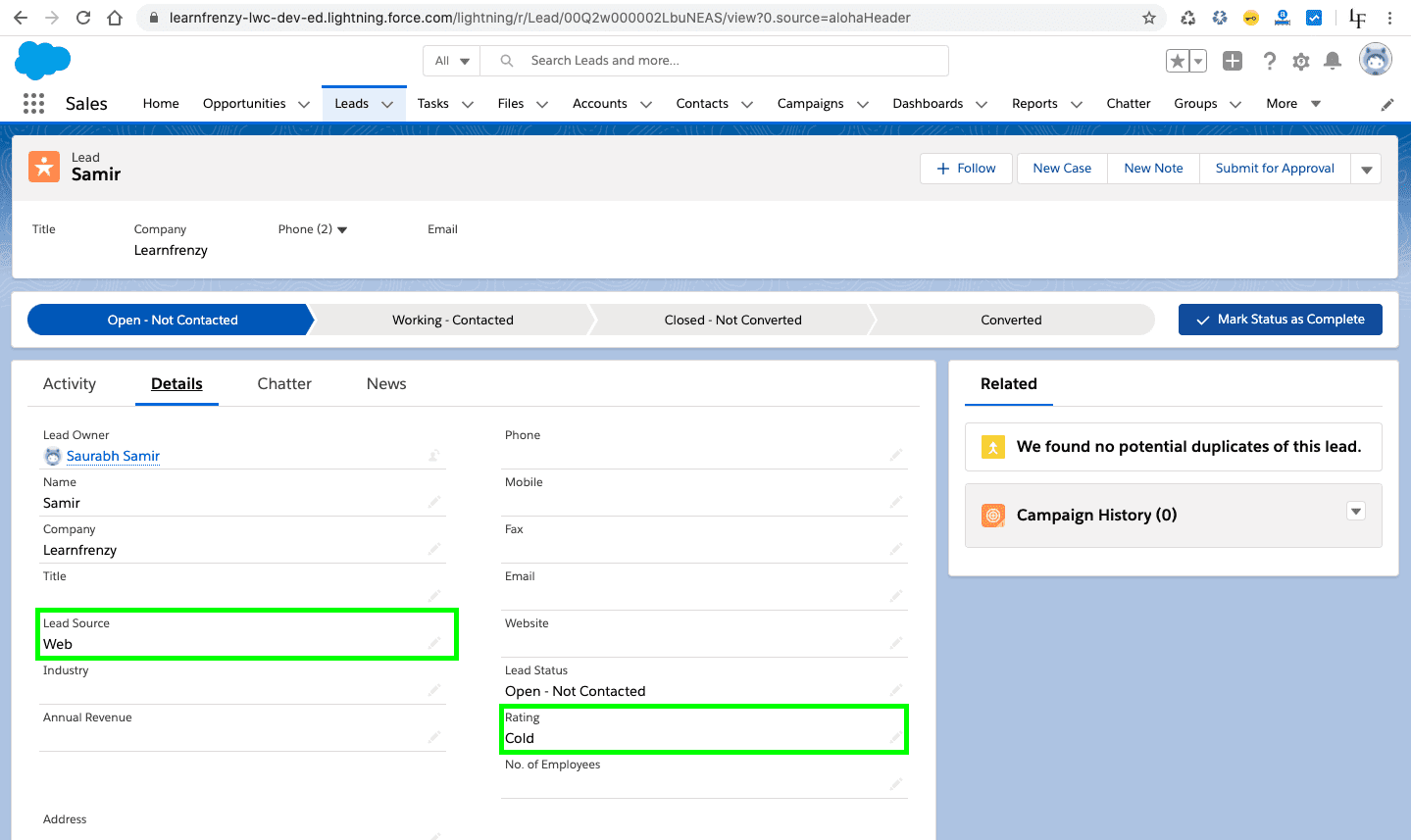
Trigger Scenario 2 :
When ever Lead is created with LeadSource as Web then give rating as cold otherwise hot.
Object : Lead
Trigger: Before Insert
Trigger Code: LeadScenario.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | trigger LeadScenario on Lead (before insert) { for(lead ld : trigger.new){ if(ld.leadsource == 'Web'){ ld.Rating = 'Cold'; } else{ ld.Rating = 'Hot'; } } } |
Output:
–> Lead is created with LeadSource as Web :
–> Before Insert :
As per the requirement, we are performing an operation on the trigger when the user save the new lead that means we need to use as before insert trigger.
Here the user has selected the lead source as 'web', so the rating will be 'cold'
Trigger Scenario 3 :
Whenever New Account Record is created then needs to create associated Contact Record automatically.
Object : Account
Trigger: After Insert
Description : When ever new Account record is successfully created, then create the corresponding contact record for the account with:
account name as contact lastname
account phone as contact phone
Trigger Code: AccountAfter.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | trigger AccountAfter on Account (after insert) { List<contact> cons=new List<contact>(); for(Account acc: Trigger.New){ Contact c=new Contact(); c.accountid=acc.id; c.lastname=acc.name; c.phone=acc.phone; cons.add(c); } insert cons;} |
Test Class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | @isTestprivate class AccountAfterHandler { @isTest static void testme(){ Integer count=[select count() from Account]; Integer size=[select count() from Contact]; Account acc=new Account(Name='LearnFrenzy',phone='022-845454'); try{ insert acc; }catch(Exception e){ System.debug(e); } Integer newCount=[select count() from Account]; Integer newsize=[select count() from Contact]; Contact c=[select lastname,phone from Contact where accountid=:acc.id]; System.assertEquals(c.lastname,acc.name); System.assertEquals(c.phone,acc.phone); }} |
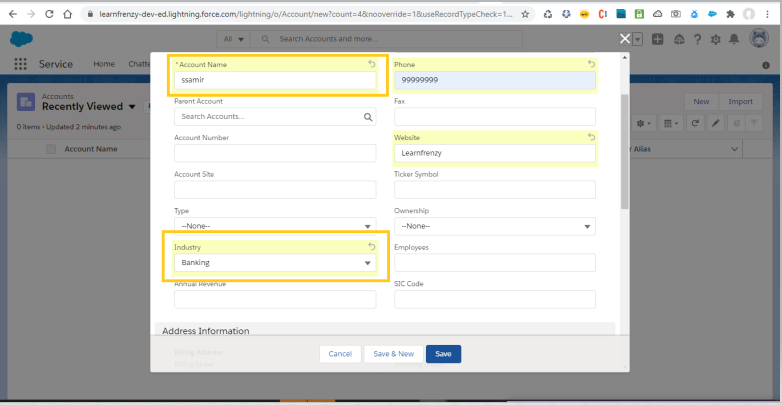
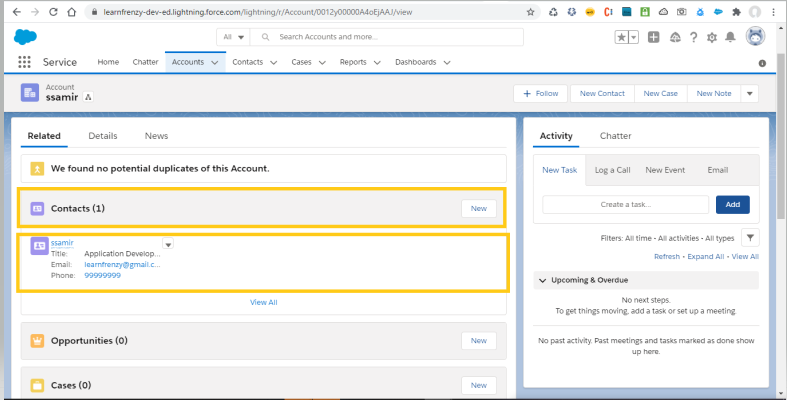
Trigger Scenario 4 :
When ever the Account is created with Industry as Banking then create a contact for account, Contact Lastname as Account name and contact phone as account phone.
Object : Account
Trigger: After Insert
Trigger Code: CreateAccountContact.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | trigger CreateAccountContact on Account (after insert) { list<contact> contacts = new list<contact>(); for(account acc : trigger.new){ if(acc.Industry == 'Banking'){ contact con = new contact(); con.LastName = acc.name; con.Phone = acc.Phone; con.AccountId = acc.Id; contacts.add(con); } } insert contacts;} |
Output:
–> New Account is created with Industry as Banking :
–> After Insert :
As per the requirement, we are performing an operation on the trigger when the user save the new account that means we need to use as after insert trigger.
AFTER triggers are usually used when information needs to be updated in a separate table/object due to a change. They run after changes have been made to the database (not necessarily committed).
Trigger Scenario 5 :
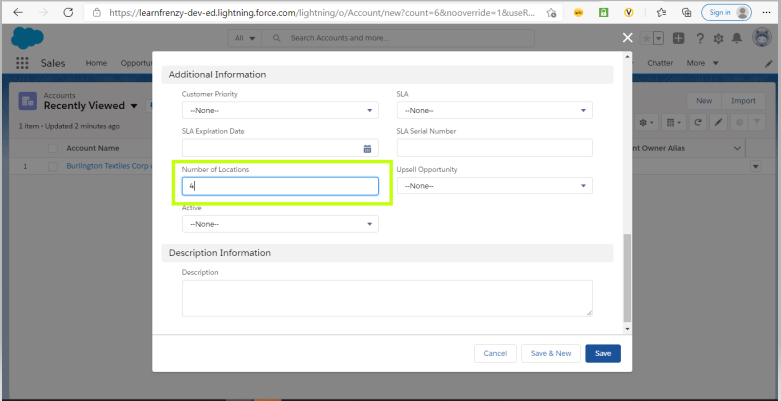
Creates the number of contacts which are equal to the number which we will enter in the Number of Locations field on the Account Object.
Create Custom field called “Number of Locations” on the Account Object (Data Type=Number)
Object : Account
Trigger: After Insert
Trigger Code: ContactsCreation.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | trigger ContactsCreation on Account (after insert) { list<contact> listContact = new list<contact>(); map<id,decimal> mapAcc = new map<id,decimal>(); for(Account acc:trigger.new){ mapAcc.put(acc.id,acc.NumberofLocations__c); } if(mapAcc.size()>0 && mapAcc!=null){ for(Id accId:mapAcc.keyset()){ for(integer i=0;i<mapAcc.get(accId);i++){ contact newContact=new contact(); newContact.accountid=accId; newContact.lastname='contact'+i; listContact.add(newContact); } } } if(listContact.size()>0 && listContact!=null) insert listContact; } |
Output:
–> Enter in the Number of Locations field on the Account Object. :
Here the user has created a new account 'LearnFrenzy' and the Number of Locations is 4.
–> After Insert :
As per the requirement, we are performing an operation on the trigger when the user creates the number of contacts which are equal to the number which we will enter in the Number of Locations field on the Account Object. That means we need to use as after insert trigger.
Trigger Scenario 6 :
When ever Opportunity "Stage" is modified to "Closed Won" then set "Close Date" as "Today Date" and "Type" as "New Customer".
Object : Opportunity
Trigger: Before Update
Trigger Code: OpportunityUpdate.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | trigger OpporUpdate on Opportunity (before update) { Map<Id,Opportunity> oppOld = Trigger.oldMap; Map<Id,Opportunity> oppNew = Trigger.newMap; Set<Id> keys =oppOld.keySet(); for(Id rid :keys){ Opportunity oldOpportunity = oppOld.get(rid); Opportunity newOpportunity = oppNew.get(rid); if(oldOpportunity.stagename!='Closed Won' && newOpportunity.stagename=='Closed Won'){ newOpportunity.closeDate=System.today(); newOpportunity.type='New Customer'; } } } |
Output:
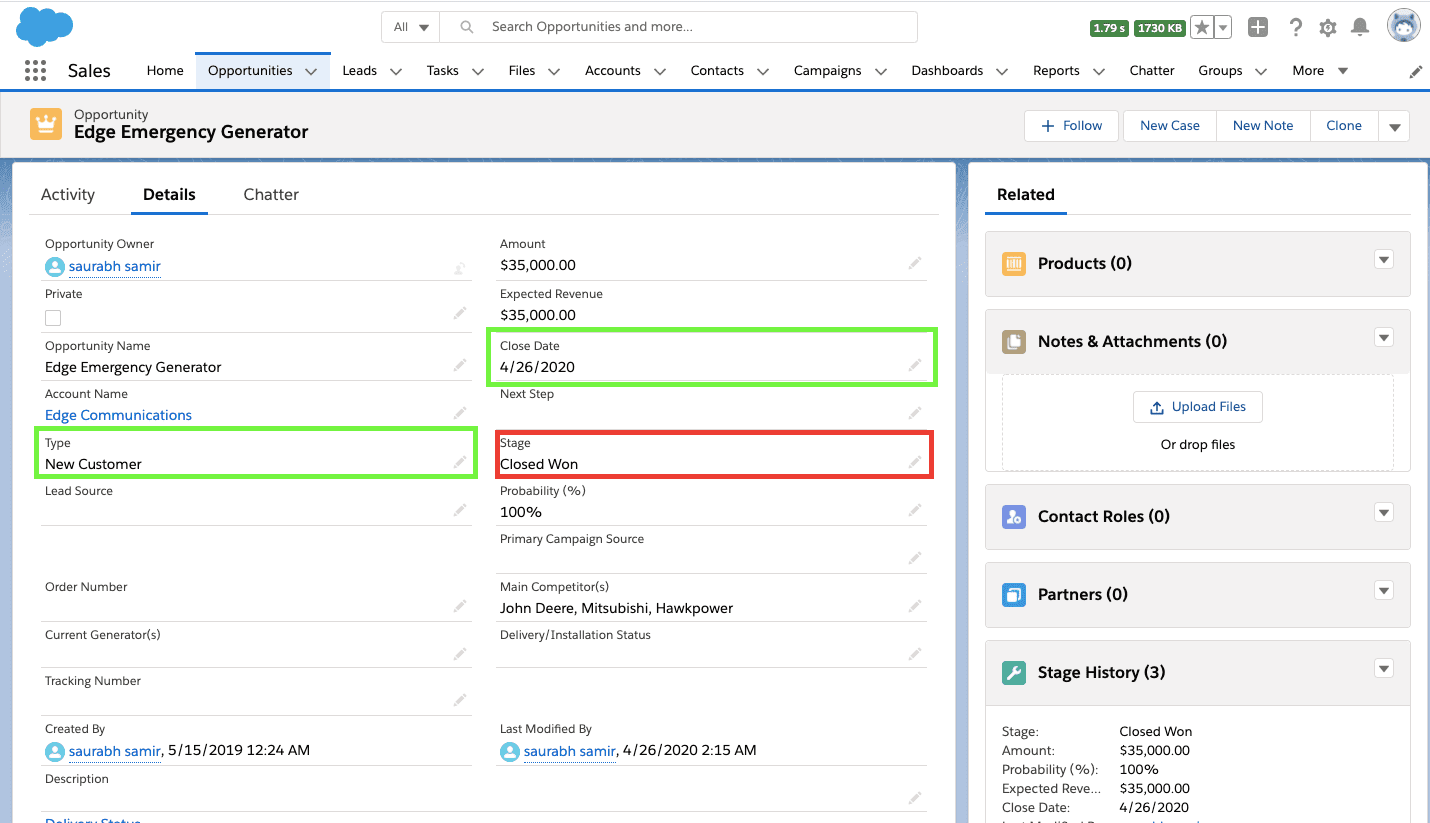
–> Opportunity "Stage" name is modified to Closed Won :
For Below Example:
Stage -> Closed Won
Closed Date -> 5/17/2019
Type -> Existing Customer - Replacement
–> Before Update :
As per the requirement, we are performing an operation on the trigger when the user modified the stage name that means we need to use as before update trigger.
Here the user has modified the "Stage" name as 'Closed Won', so before update the "Type" will be 'New Customer' and "Closed Date" will be "Today Date".
Trigger Scenario 7 :
when a new contact is created for a existing account then set contact otherphone as account phone.
Object : Contact
Trigger: Before Insert
Trigger Code: ContactAccountRelation.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | trigger ContactAccountRelation on Contact (before insert) { Set<Id> accIdSet = new Set<Id>(); for(Contact con : trigger.new){ if(String.isNotBlank(con.AccountId)){ accIdSet.add(con.AccountId); } } if(accIdSet.size() > 0){ Map<Id,Account> accMap = new Map<Id,Account>([Select Id, Phone From Account where id In:accIdSet]); for(Contact con : trigger.new){ if(con.AccountId != null && accMap.containskey(con.AccountId)){ if(accMap.get(con.AccountId).Phone != null){ con.OtherPhone = accMap.get(con.AccountId).Phone; } } } }} |
Output:
–> Existing Account :
Account Name* : Learnfrenzy
Phone: +91-9999-888-777
–> Before Insert :
As per the requirement, we are performing an operation on the trigger when the user create new contact is created for a existing account then set contact otherphone as account phone that means we need to use as before insert trigger.
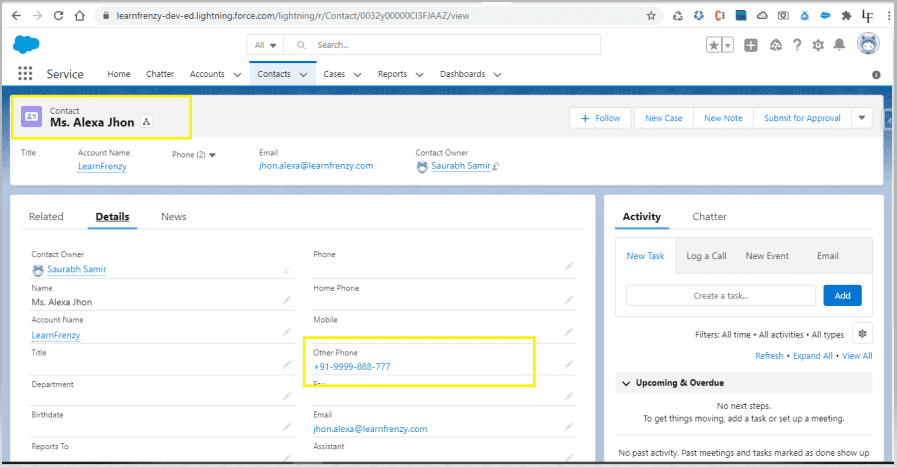
–> New Contact :
Account Name* : Learnfrenzy
Contact : Ms. Alexa Jhon
Other Phone : +91-9999-888-777
Trigger Scenario 8 :
The following Trigger will fires when we try to create the account with same name i.e. Preventing the users to create Duplicate Accounts
Object : Account
Trigger: Before Insert, Before Update
![]() MIND IT !
MIND IT !
Here (Way-1), I have used SOQL inside for loop which will affect governor limit and it is not best practice.
The most important being that it is not bulkified. We should always avoid SOQL inside loop. So please see second way-2 below for best practices.
WAY-1
Trigger Code: AccountDuplicateTrigger.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | trigger AccountDuplicateTrigger on Account (before insert, before update) { for(Account a:Trigger.new) { List<Account> acc=[select ID from account where Name=:a.Name and Rating=:a.rating]; if(acc.size()>0) { a.adderror('You cannot create a duplicate account'); } }} |
Test Class: AccountDuplicateTriggerTest
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | @istestpublic class AccountDuplicateTriggerTest{ static testmethod void myTest(){ Boolean result =false; Account a = new Account(); a.Name= 'Learnfrenzy'; a.Rating='Warm'; insert a; try{ Account a1=new account(); a1.Name= 'Learnfrenzy'; a1.Rating='Warm'; insert a1; } catch(DMLException ex) { result=true; system.assert(result); } } } |
Output:
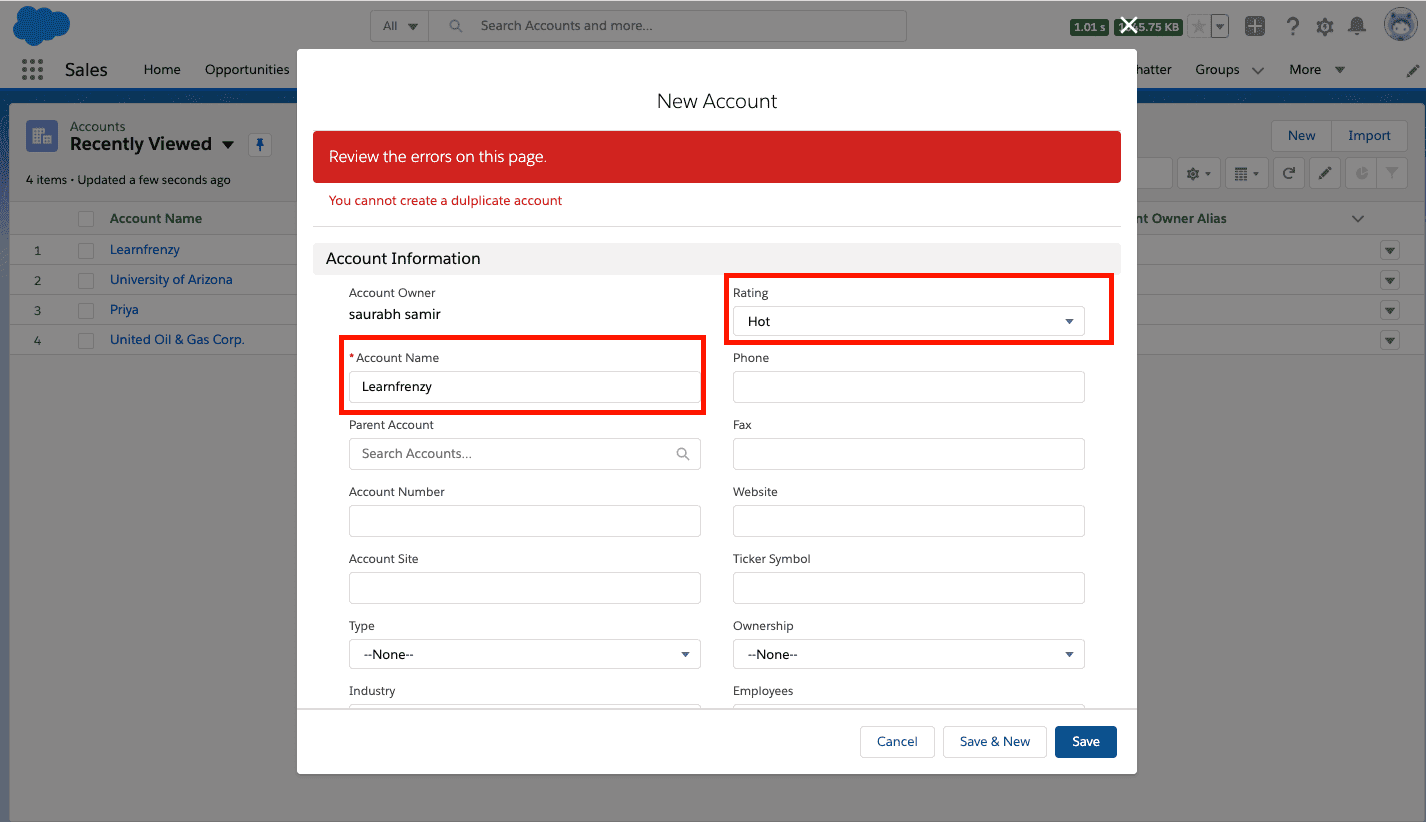
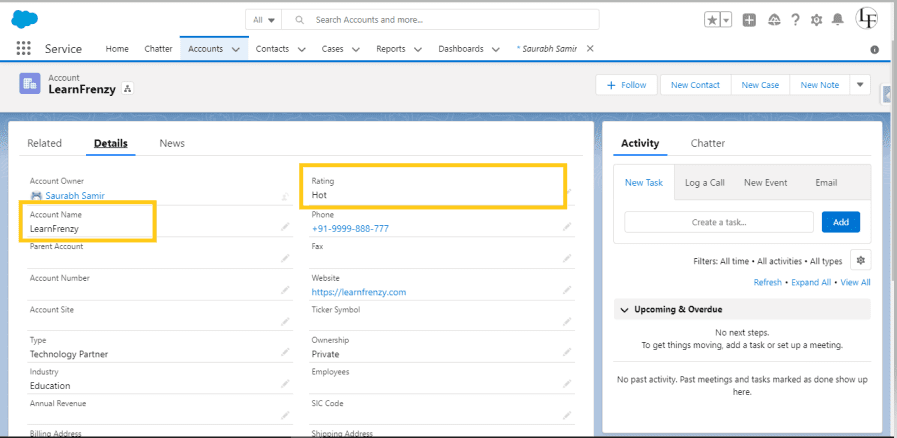
–> Existing Account :
Account Name* : Learnfrenzy
Rating: Hot
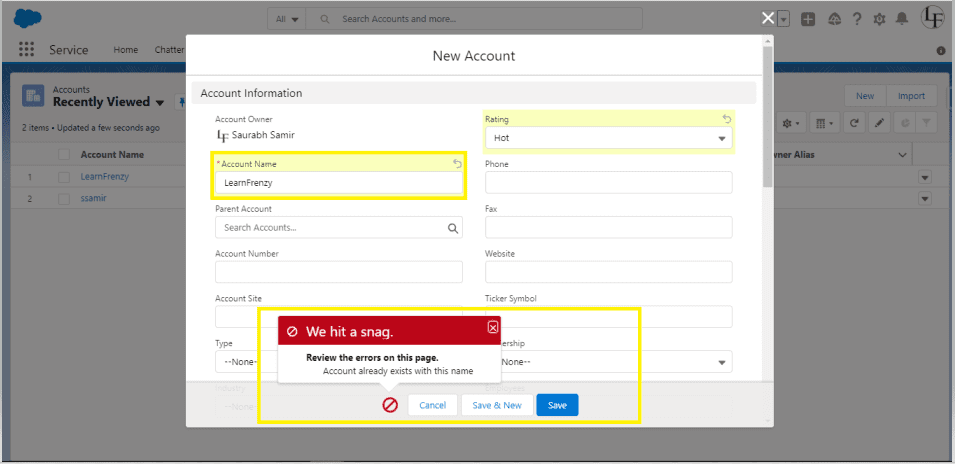
–> when we try to create the account with same name i.e. Preventing the users to create Duplicate Accounts (before insert, before update) :
WAY-2 :Here, avoid SOQL Queries or DML statements inside FOR Loops
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | trigger AccountDuplicateTrigger on Account (before insert, before update) { list<string> acc = new list<string>(); for(Account a:Trigger.new) { acc.add(a.name); } list<Account> listOfDuplicateAccounts = [select id, Name from Account where Name in :acc]; for(Account account:trigger.new) { if(trigger.isInsert){ if(listOfDuplicateAccounts.size()!=0) { account.addError('Account already exists with this name'); } } if(trigger.isUpdate) { for(Account oldaccount :trigger.old) { if(account.Name!=oldAccount.Name && listOfDuplicateAccounts.size()!=0) { account.addError('Account already exists with this name'); } } } } } |
Output:
–> Existing Account :
Account Name* : Learnfrenzy
Rating: Hot
–> when we try to create the account with same name i.e. Preventing the users to create Duplicate Accounts (before insert, before update) :
As like as this code you can write Trigger to prevent from creating Duplicate Records in your object.
Trigger Scenario 9 :
Write a trigger in which if an account that has related contacts and the user tries to delete that account it throws you an error "Account cannot be deleted".
Object : Account
Trigger: Before Delete
Trigger Code: PreventAccountFromDeletion.apxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | trigger PreventAccountFromDeletion on Account (before delete){ List<account> accList = new List<account>(); Set<id> accIdSet = new Set<id>(); for(Account acc : Trigger.old) { accIdSet.add(acc.id); } Map<Id, Account> accts = new Map<Id, Account>([Select Id, (Select Id from contacts) from Account where id in :accIdSet]); for(Account acc : Trigger.old) { if(accts.get(acc.id).contacts.size()>0) { acc.adderror('Account cannot be deleted'); } } } |
Output:
–> Account :
Account Name* : LearnFrenzy - Salesforce
Contacts(2):
Saurabh Samir
Azusa Zeal
Open a account record in your Salesforce org. Click on the inverted triangle icon located on the top-right of the account record. It will open a dropdown, click on the ‘Delete’.
–> Before Delete :
As per the requirement, account that has related contacts should not be deleted. That means we need to use as Before Delete trigger.
It will prompt you to confirm the delete action by clicking on the ‘Delete’ button.
As soon as you click on the button, you will see the error message which we wrote in our trigger class that ‘Account cannot be deleted’.
Trigger Scenario 10 :
Write a trigger on lead to prevent duplicate records based on lead email, if a record already created with the same Email, Or record is Updated. The trigger should throw an error.
Standard Object : Lead
Trigger: Before Insert, After Insert, Before Update, After Update
Trigger Code: DuplicateEmailsInLead.apxt (Apex Class Trigger)
It will be fired whenever New Lead is Created Or Updated
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | trigger DuplicateEmailsInLead on Lead (before insert, after insert, before update, after update) { if(trigger.isBefore){ if(trigger.isInsert){ leadHandlerController.updateInsertLead(trigger.new); } if(trigger.isUpdate){ leadHandlerController.updateInsertLead(trigger.new); } } else if(trigger.isAfter){ system.debug('I am inside of after method'); } } |
Apex Class Controller: leadHandlerController.apxc
Apex handler trigger to prevent duplicate records based on lead email.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | public class leadHandlerController { public static void updateInsertLead(List<Lead> leadObjList){ Set<String> leadSet= new Set<String>(); List<Lead> leadObj = new List<Lead>(); List<Lead> leadList=[Select Id, Name, Email, Phone From Lead Where Email != null]; for(Lead d1:leadList){ leadSet.add(d1.Email); } for(lead e1:leadObjList){ if(leadSet.contains(e1.Email)){ e1.Email.addError('Do not allow duplicate Email'); } } }} |
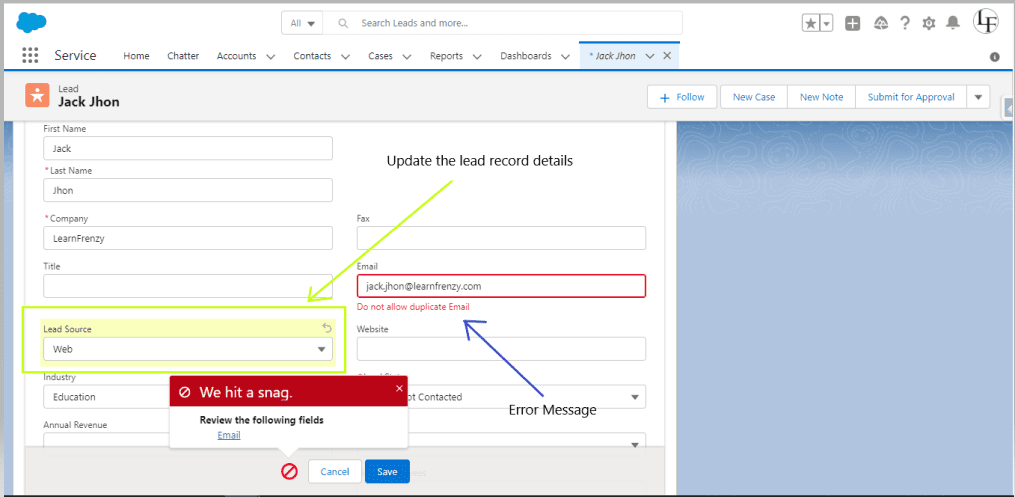
Output:
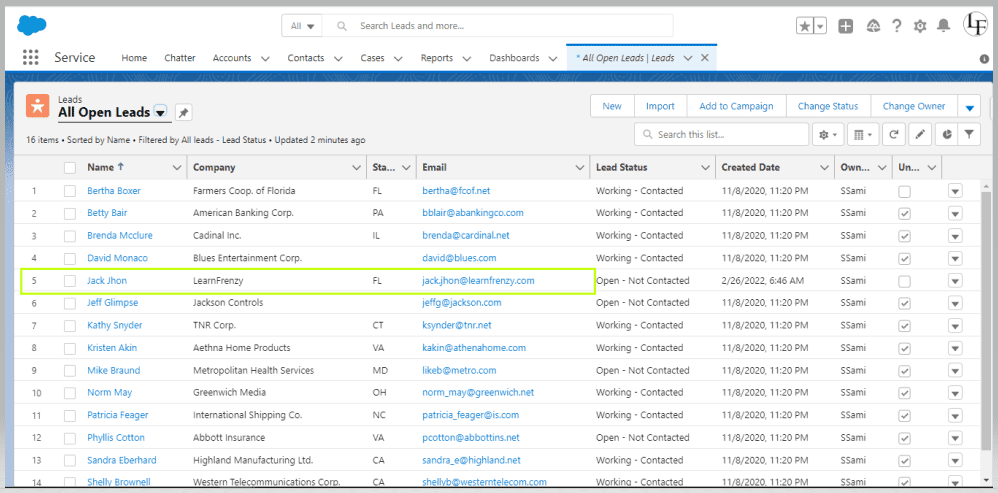
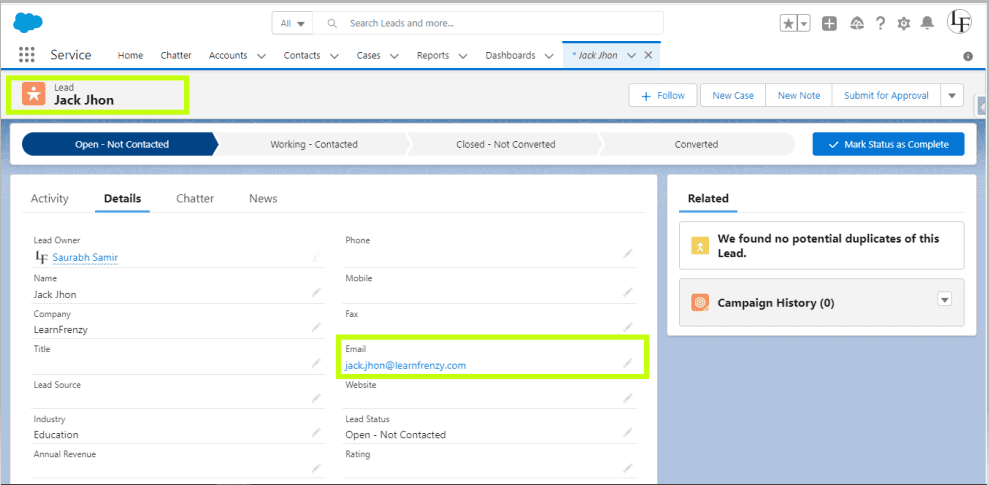
–> Lead Record Page :
Name : Jack Jhon
Email : jack.jhon@learnfrenzy.com
The below example is based on trigger on lead to prevent duplicate records based on lead email, if a record already created with the same Email, Or record is Updated. The trigger should throw an error.
--> When updating a lead source in an existing record, where the email already exists.
Trigger Scenario 11 :
A salesforce company named ABC and plan to launch a product in different region (ASIA, EMEA, NA, SA) across the globe.They also want to sell the products to their clients which are in ASIA,EMEA, NA and SA .
From Admin point of view this particular scenario need to be logged into CRM for:
Create a Multi picklist name In Account Object “Working in”
Picklist Values:
1. ASIA
2. EMEA
3. NA
4. SA
(I) Write a script to get the total Quantity of Products sold in only Accounts Working in = ASIA.
(II) Write a Trigger to stop creating or updating Opportunities with Account having “Working in = ASIA” and Already 2 Closed Won Opportunity under same Account.
Solution :
Script : (I) Write a script to get the total Quantity of Products sold in only Accounts Working in = ASIA.
First we will create a Multi picklist name In Account Object “Working in”. After creation you can see the filed name.
OBJECT : Account
FIELD LABEL : Working in
FIELD NAME : Working_in__c
DATA TYPE : Picklist (Multi-Select)
OBJECT : Opportunity
FIELD LABEL : Quantity
FIELD NAME : TotalOpportunityQuantity (Default in Opportunity Object)
DATA TYPE : Number(16, 2)
Apex Class: GetProductQuantity.apxc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | public class GetProductQuantity { public static void GetToatlProductQty(){ List<account> AccList = [select id,Name from Account where Working_in__c = 'ASIA']; //system.debug('ACCCC'+AccList); if(AccList.size()>0){ List<Opportunity> oppList =[select id,TotalOpportunityQuantity,AccountId from Opportunity where AccountId IN: AccList AND StageName='Closed Won']; //system.debug('opp'+oppList); for(Opportunity opp:oppList){ System.debug('ACCOUNT'+opp.AccountId+'Number Of Product Sol'+opp.TotalOpportunityQuantity); } } } } |
To readers:If you find any mistakes let me know














No comments:
Post a Comment