1. Is it possible to write a validation rule which will fire only on insert of record not on update of record ?
Use isnew() function which checks if the formula is running during the creation of a new record and returns TRUE if it is. If an existing record is being updated, this function returns FALSE.
2. Is it possible to schedule a dynamic dashboard in Salesforce?
No, it is not possible to schedule a dynamic dashboard in Salesforce.
3. Is it possible to write a validation rule on record delete?
No, only in insert and update events you can write validation rule.
4. Difference between formula field and rollup summary in Salesforce ?
- Rollup Summary field is used to calculate the sum of a fields in the child object record.
- It is compulsory to be in a Master-Detail relationship to use the rollup summary.
- A rollup summary field is always created on Master record. (Parent to Child).For example. You have an Account and multiple Contacts under that Account. Each of the Contact have a number field on it say Contacted People. Now on the Account you can create a Rollup summary to check the Number of Contacted People via all your contacts.
- Where else a formula field is mostly used for calculations within a certain object. And it is child to Parent.
5. Is there any standard object which is also act as junction object ?
Yes, there are some standard objects which acts as a junction object.
For Example, Standard object OpportunityContactRole is acts as junction object between Opportunity and Contact objects.
6. What is the default DateTime format of Salesforce ?
DateTime:
- Salesforce stores all DateTimes in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) format.
- Remember that dateTime field values are stored as Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
- When one of these values is returned in the Salesforce application, it is automatically adjusted for the timezone specified in your organization preferences.
- Your application may need to handle this conversion.
Date:
- Date fields contain no time information and completely ignore timezones.
- Whatever date you specify when you set it will be the date every user sees, with any time and zone information being ignored.
7. How to insert null values into Dataloader ?
Go to data loader -> setting -> check Is null values checkbox.
8. Maximum batch size of data loader?
200
9. What is the purpose or use of @TestVisible?
- Use the TestVisible annotation to allow test methods to access private or protected members of another class outside the test class.
- These members include methods, member variables, and inner classes.
- Using this annotation, you do not have to change the access modifiers of your methods and member variables to public if you want to access them in a test method.
- For example, if a private member variable isn’t supposed to be exposed to external classes but it should be accessible by a test method, you can add the TestVisible annotation to the variable definition.
10. What is the difference between trigger and workflow in Salesforce ?
Workflow:
- Workflow will be helpful to update the same object or master object in custom master-detail relationships.
- Coding is not required.
- Workflow actions are Field Update, Email alert, Task alert and outbound message.
- We cannot use SOQL query from database on workflow.
- We cannot fire workflows after record has been deleted.
Trigger:
- Trigger can work across objects.
- Coding is required.
- Trigger executes before or after these types of operations insert, update, delete, merge, upsert & undelete.
- We can use SOQL’s from data base in one trigger.
- We can fire Trigger after record has been deleted.
11. What is fiscal year in salesforce ?
Salesforce allows two types:
Standard Fiscal Years are periods that follow the Gregorian calendar, but can start on the first day of any month of the year. (A Gregorian Year is a calendar based on a 12 Month Structure and is used throughout much of the world.)
Custom Fiscal Years are for companies that break down their fiscal years, quarters and weeks in to custom fiscal periods based on their financial planning requirements.
Note: After you enable custom fiscal years, you cannot disable the feature. However, if you need to revert to standard fiscal years, you can define custom fiscal years that follow the same Gregorian calendar structure as the Salesforce standard fiscal years.
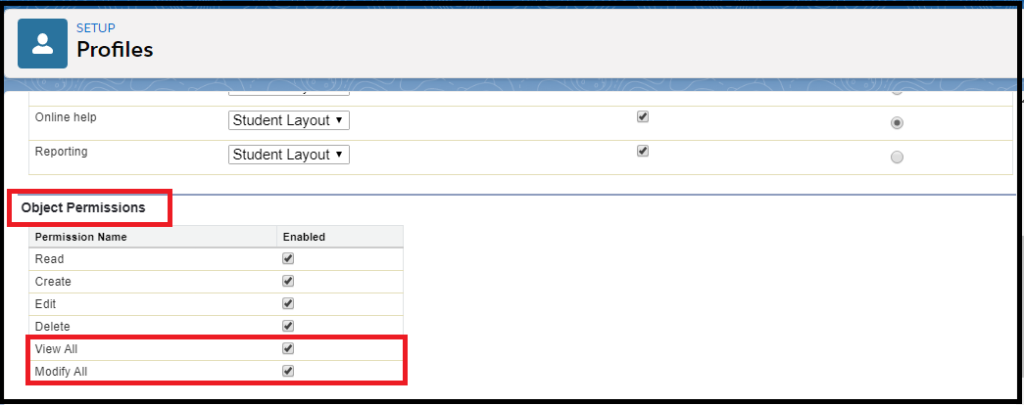
12. What is the difference between Role and Profile in Salesforce ?
Role control record level access can be controlled by Role.
Profiles control the objects level access settings.
In simple words, Profile defines what user can do in your salesforce org and Role defines what user can see. Other difference is, Profile is mandatory, Role is not.
13. Will data be lost in a custom field if data type is changed to number from any other data type?
Yes
Changing the data type of an existing custom field can cause data loss in the following situations:
- Changing to or from type Date or Date/Time
- Changing to Number from any other type
- Changing to Percent from any other type
- Changing to Currency from any other type
- Changing from Checkbox to any other type
- Changing from Picklist (Multi-Select) to any other type
- Changing to Picklist (Multi-Select) from any other type. Currently defined picklist values are retained when you change a picklist to a multi-select picklist. If records contain values that are not in the picklist definition, those values are deleted from those records when the data type changes.
- Changing from Auto Number to any other type
- Changing to Auto Number from any type except Text
- Changing from Text to Picklist
- Changing from Text Area (Long) to any type except Email, Phone, Text, Text Area, or URL.
14. There is one field which is used in Lead conversion and I want to convert its data type, is this possible?
No, You can not change the data type of any custom field that is mapped for lead conversion.
15. Can we convert formula field into any other data type ?
No, Formula fields are special read-only fields that cannot be converted to any other data type. Likewise, you cannot convert any other field type into a formula field.
16. What is Web-to-Lead in Salesforce ?
In simple words, Web-to-Lead is Generate Leads from Your Website for Your Sales Teams. This feature create or generate upto 500 leads per day with prospecting data from your company’s website visitors.
Salesforce runs field validation rules before creating records submitted via Web-to-Lead and only creates records that have valid values.
If a new lead cannot be generated due to errors in your Web-to-Lead setup, Customer Support is notified of the problem so that we can help you correct it.
17. What is the Web-to-Case in Salesforce?
In simple word, Capture Cases from your Website.
Gather customer support requests directly from your company’s website and automatically generate up to 5,000 new cases a day with Web-to-Case. This can help your organization respond to customers faster, improving your support team’s productivity.
Use a simple web form or a self-service customer community to make it easy for customers to submit cases directly to your customer support group.
Keep these considerations in mind:
- Whenever possible, Web-generated cases are automatically linked to the relevant contact and account based on the customer’s email address.
- Salesforce runs field validation rules before creating records submitted via Web-to-Case and only creates records that have valid values. All universally required fields must have a value before a record can be created via Web-to-Case.
- Salesforce doesn’t support rich text area (RTA) fields on Web-to-Case forms.
- If you exceeded the daily limit and you want to increase that limit then go to Help & Training and raise a case with salesforce.
18. What are the Types of Sharing Rules in Salesforce and explain it?
Account Sharing Rules:
- Based on who owns the account.
- Set default sharing access for accounts and their associated cases, contacts, contracts, and opportunities.
Contact Sharing Rules:
- Based on who owns the contact (must be associated with an account).
- Set default sharing access for individual contacts and their associated accounts Cannot use with: Territory Management and B2I (Person Account) enabled orgs
Opportunity Sharing Rules (EE/UE):
- Based on who owns the opportunity.
- Set default sharing access for individual opportunities and their associated accounts.
Case Sharing Rules (EE/UE):
- Based on who owns the case.
- Set default sharing access for individual cases and associated accounts
Lead Sharing Rules (EE/UE):
- Based on who owns the lead.
- Set default sharing access for individual leads
Custom Object Sharing Rules (EE/UE):
- Based on who owns the custom object.
- Set default sharing access for individual custom object records
19. How many rows return by list controller?
10000 records
20. How can we check the object accessibility on visualforce page?
Answer: {!$ObjectType.MyCustomObject__c.accessible}
21. What are the different AJAX action tags? What does each do?
actionStatus: used to display start and stop statuses of AJAX requests.
actionSupport: used to call a second component when an event happens to the first component.
actionPoller: similar to actionSupport, but the event is based on a timer instead of a user action.
actionFunction: provides support for invoking a controller action from JavaScript code using an AJAXrequest by defining a new JavaScript function.
actionRegion: used to demarcate which parts of the page the server should reprocess.
22. How many ways call controller from visualforce page ?
- Command button
- Command link
- Javascript remoting
- Actionpoller
- ActionFunction.
23. What is the size of view state in salesforce ?
135 KB
24. Does Javascript remoting is part of view state ?
NO
25. I want to count how many times execute() method executed in Batch class ?
With the help of Database.stateful
Implementing database.stateful will maintain your state so the map that you are using in execute method will contain all the error messages after the completion of execute method. In finish method you will have aggregate of all errors that can be finally used.
26. Compare JavaScript Remoting and <apex:actionFunction> ?
The <apex:actionFunction> component also lets you call controller action methods through JavaScript.
In general, <apex:actionFunction> is easier to use and requires less code, while JavaScript remoting offers more flexibility.
Here are some specific differences between the two :
The <apex:actionFunction> tag:
- lets you specify rerender targets
- submits the form
- doesn’t require you to write any JavaScript
JavaScript remoting:
- lets you pass parameters
- provides a callback
- requires you to write some JavaScript
27. Difference between count() and count(fieldname) ?
For COUNT(), the query result size field returns the number of rows. The records field returns null.
COUNT(fieldName) returns the number of rows that match the filtering conditions and have a non-null value for fieldName.
28. What are the Best Practises for Improving Visualforce Performance ?
1) The view state size of your Visualforce pages must be under 135 KB. By reducing your view state size, your pages can load quicker and stall less often.
2) Large page sizes directly affects load times. To improve Visualforce page load times:
Cache any data that is frequently accessed, such as icon graphics.
Avoid SOQL queries in your Apex controller getter methods.
Reduce the number of records displayed on a page by adding filter condition in SOQL
3) Reduce Multiple Concurrent Requests: use <apex:actionpoller>
4) By using the with sharing keyword when creating your Apex controllers, you have the possibility of improving your SOQL queries by only viewing a data set for a single user.
5) Preventing Field Values from Dropping Off the Page.
29. What are the Salesforce best practices for apex?
- Bulkify your Code
- Avoid SOQL Queries or DML statements inside FOR Loops
- Bulkify your Helper Methods
- Using Collections, Streamlining Queries, and Efficient For Loops
- Streamlining Multiple Triggers on the Same Object
- Querying Large Data Sets
- Use of the Limits Apex Methods to Avoid Hitting Governor Limits
- Use @future Appropriately
- Writing Test Methods to Verify Large Datasets
- Avoid Hardcoding IDs.
30. What is the difference between force.com and Salesforce.com?
Force.com is Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Salesforce.com is Software as a Service (SaaS)
31. What is a report type?
A report type is a skeleton over which you can build the report. It specify the structure of your report(Object relationship).
- Salesforce provides standard report types using which reports can be build.
- If the standard type does not suffice your requirement then we have to go for custom report type.
- It allows to build framework from which reports can be created. While building report type we need to select object and the relationship between objects to display in report. Which fields will be available for display can also be set.
32. What are analytical snapshot?
Analytical snapshots can be used to schedule a report run and then save the report result as records in custom object.
- While building a analytical snapshot we have to select a source report and destination object.
- Then map the fields from report and object. The report runs at specified time and then inserts the report result as records in that object.
- Advantages that we get through analytical snapshot are as below, Runs reports faster, Sort and filter data using list views, can view trend in data via object records.
- The object selected for record insertion should not have any insert trigger on it.
33. What are various standard exceptions that salesforce throws?
Salesforce throws number of standard exception .
Some of the important ones are as below:
- dmlexception,
- listexception,
- email exception,
- calloutexception,
- JSONexception,
- mathexception,
- Queryexception,
- sObjectexception,
- xmlexception,
- typeexception,
- visualforceexception,
- stringexception,
- searchexception,
- nullpointerexception,
- noaccessexception.
34. What are the various ways of deployment in salesforce?
Metadata components in salesforce can be deployed using various ways as below
35. How can you expose a apex class as web service? and how to obtain a wsdl file for exposed class?
In order to expose a class as a webservice we have to use keyword ‘webservice’ with the method also the method should be global and also the class should be defined global. ex-
Global class DemoWebServiceClass{
global webservices void myWebServiceMethod(){
}
}
A wsdl file for a apex class can be obtained by using the button generate wsdl on class.
36. What is an account team?
Account team is group of users that work on a articular account. The users in a account team can be given access depending on the need. A account team appears as related list on account.
37. What are the Different API’s in salesforce ?
Chatter REST API :
Chatter REST API provides programmatic access to Chatter feeds and social data such as users, groups, followers, and files. Use Chatter REST API to integrate Chatter into a variety of applications such as mobile applications, third-party Web apps and intranet sites.
REST API :
This api is used for accessing objects in organization through REST. Data format used is JSON, XML and communicates Synchronously. We can use this whenever we want to leverage the REST architecture to integrate with the salesforce environment. There is No WSDL required while using REST API. This is well-suited for browser based applications, mobile appslication, and social apps they are more interactive. It is uses REST protocol.
BULK API :
The Bulk API provides a programmatic option to quickly load your org’s data into Salesforce. Bulk API is based on REST principles and is optimized for loading or deleting large sets of data. You can use it to query, queryAll, insert, update, upsert, or delete many records asynchronously by submitting batches. Salesforce processes batches in the background.
SOAP API :
SOAP API provides a powerful, convenient, and simple SOAP-based web services interface for interacting with Salesforce. Protocol used is SOAP/WSDL, format is XML and communicates Synchronously. You can use SOAP API to create, retrieve, update, or delete records. You can also use SOAP API to perform searches and much more. Use SOAP API in any language that supports web services.
METADATA API :
Metadata API is intended for managing customizations and for building tools that can manage the metadata model, not the data itself. Here the SOAP API is oriented around accessing data and manipulating records, the Metadata API’s focuses on metadata. It gives you an API to manipulate layouts, classes, visualforce pages, Apex triggers. Protocol used is SOAP/WSDL. Format used is XML and communicates Asynchronously.
Tooling API :
This is used when one wants to manage and deploy working copies of Apex classes or triggers or Visualforce pages or other components.
Streaming API :
Use Streaming API to receive notifications for changes to Salesforce data that match a SOQL query you define, in a secure and scalable way. This enables one to reduce the number of API calls and improve performance.
38. What is the default batch size if we enable bulk API?
2,000 records.
39. What is recursive workflow rule? How to avoid recursive workflow rules?
Whenever you enable Re-evaluate Workflow Rules after Field Change checkbox in the Field Update of a workflow rule, due to this field update other workflow rules on the same object will be fired if the entry criteria of those workflow rules satisfied.
And , You have other workflow rules also if you enable Re-evaluate Workflow Rules after Field Change checkbox in the Field Update recursive workflow rules will come in some scenarios.
We can take two steps to avoid recursive workflow rules :
- For the workflow Evaluation Criteria if you choose created, and any time it’s edited to subsequently meet criteria option, we can avoid recursive workflow rules.
- If you don’t enable Re-evaluate Workflow Rules after Field Change checkbox in the Field Update of a workflow rule we can avoid.
40. What is the difference between database.insert and insert?
Both DML statements perform same operation i.e. insert records.
Insert is the DML statement which is same as databse.insert.
However, database.insert gives more flexibility like rollback, default assignment rules etc. we can achieve the database.insert behavior in insert by using the method setOptions(Database.DMLOptions).
Important Difference:
If we use the DML statement (insert), then in bulk operation if error occurs, the execution will stop and Apex code throws an error which can be handled in try catch block.
If DML database methods (Database.insert) used, then if error occurs the remaining records will be inserted / updated means partial DML operation will be done.
41. What is the difference between 15 digit and 18 digit IDs in Salesforce?
- 15 digit ID in salesforce.com is case sensitive and 18 Digit Id is case-insensitive.
- Many applications does not support case sensitive strings, so in that case we can make use of 18 digit Id which is case in-sensitive.
- 15 digit Id number will have numeric digits range from (0–9), a Lowercase letter(a-z) or a Uppercase letters(A-Z).
- 15 digit ID in salesforce.com is case sensitive. Example 999999999999ABC is different from 999999999999abc.
- When using external productive tools like Microsoft Excel, MS Access and SQL Server external ID’s are not case sensitive and they don’t recognize the difference between 999999999999ABC and 999999999999abc.
- Salesforce.com has recognized this problem and Salesforce.com has established 18 digit character insensitive ID.
- This 18 Digit ID is case insensitive which is formed by adding a suffix to the 15 Character Id number.
42. What are different types of reports?
Tabular:
- Tabular reports are the simplest and fastest way to look at data.
- Similar to a spreadsheet, they consist simply of an ordered set of fields in columns, with each matching record listed in a row.
- Tabular reports are best for creating lists of records or a list with a single grand total.
- They can’t be used to create groups of data or charts, and can’t be used in dashboards unless rows are limited. Examples include contact mailing lists and activity reports.
Summary:
- Summary reports are similar to tabular reports, but also allow users to group rows of data, view subtotals, and create charts.
- They can be used as the source report for dashboard components.
- Use this type for a report to show subtotals based on the value of a particular field or when you want to create a hierarchical list, such as all opportunities for your team, subtotaled by Stage and Owner.
- Summary reports with no groupings show as tabular reports on the report run page.
Matrix:
- Matrix reports are similar to summary reports but allow you to group and summarize data by both rows and columns.
- They can be used as the source report for dashboard components.
- Use this type for comparing related totals, especially if you have large amounts of data to summarize and you need to compare values in several different fields, or you want to look at data by date and by product, person, or geography.
- Matrix reports without at least one row and one column grouping show as summary reports on the report run page.
Joined:
- Joined reports let you create multiple report blocks that provide different views of your data.
- Each block acts like a “sub-report,” with its own fields, columns, sorting, and filtering.
- A joined report can even contain data from different report types.
43. What are different kinds of dashboard component?
Table:
- Use a table to show a set of report data in column form.
- Visualforce Page: Use a Visualforce page when you want to create a custom component or show information not available in another component type.
- Custom S-Control: Custom S-Controls can contain any type of content that you can display or run in a browser, for example, a Java applet, an ActiveX control, an Excel file, or a custom HTML Web form.
Chart: Use a chart when you want to show data graphically.
Metric:
- Use a metric when you have one key value to display.
- Enter metric labels directly on components by clicking the empty text field next to the grand total.
- Metric components placed directly above and below each other in a dashboard column are displayed together as a single component.
Gauge: Use a gauge when you have a single value that you want to show within a range of custom values.
44. What is the maximum size of the PDF generated on visualforce attribute renderAs ?
15 MB
45. What is the System.runAs() ?
Generally, all Apex code runs in system mode, and the permissions and record sharing of the current user are not taken into account. The system method, System.runAs(), lets you write test methods that change user contexts to either an existing user or a new user. All of that user’s record sharing is then enforced. You can only use runAs in a test method. The original system context is started again after all runAs() test methods complete.
Example :
System.runAs(u) {
// The following code runs as user ‘nitish’
System.debug(‘Current User: ‘ + UserInfo.getUserName());
System.debug(‘Current Profile: ‘ + UserInfo.getProfileId());
}
46. What is Difference in render, rerender and renderas attributes of visualforce?
render : It works like display property of CSS. It is used to show or hide element on visualforce page.
rerender : After Ajax which component should be refreshed — This attribute is available on commandlink, commandbutton, actionsupport .
renderas : render page as PDF, DOC and Excel. With the help of this attribute you can download the data display on visualforce page.
47. When GroupBy is used, How to write or use the Where clause in SOQL ?
We cannot use the Where clause with Group By instead we will need to use the Having Clause.
48. If user does not have any right on particular record and have only read level access at object level. Can he change the record owner?
Yes. In profile, there is setting for Transfer Record.
49. Explain the use of Test.setPage() ?
It is used to set the context to current page, normally used for testing the visual force controller.
50. Can you use Group by clause inside inner query in SOQL? like SELECT Id, Name,(SELECT Count(Id),Name FROM Contacts Group By Name Having Count(Id) > 1 )
No. Only root queries support aggregate expressions. Return type is List<AggregateResult> for above query However the root result expects List<Account> and there is no syntax or provision available in Salesforce to specify that child results are of type AggregateResult.
51. What is the difference between apex:dataTable and apex:pageBlockTable components in Visualforce?
Both component is used to render data in tabular format. apex:dataTable will render records in simple HTML table format whereas the apex:pageBlockTable possess default look and feel of salesforce standard CSS and must be written inside apex:pageBlock component.
52. How to get all records even from recycle bin or Achieved Activities using SOQL query?
We will need ALL Rows clause of SOQL.
Example :
SELECT COUNT() FROM Opportunity WHERE AccountId = acc.Id ALL ROWS
53. How can you lock record using SOQL so that it cannot be modified by other user.
We will need FOR UPDATE clause of SOQL.
Example :
SELECT Id FROM Contact LIMIT 2 FOR UPDATE
54. In trigger, lets say you have system.debug() statement after adderror() method. Will system.debug() be statement executed in Trigger after adderror() method?
adderror() method is not error statement rather its normal execution flow and all the statements written after adderror() will be executed normally.
55. How to get total number of Child records in Lookup relationship?
As Rollup Summary field is only supported in Master detail, we cannot use it for Lookup.
There are following two ways.
1. Inline Visualforce page
2. Trigger on Child Object, which will update field in Parent record if child record is inserted, deleted or undeleted.
If anyone has any other idea please comment. I will add that too.
56. What will happen if you try to update record in After Trigger Context?
You will get an error saying record is Read only.
57.How to get IP Address of User in Apex?
String ipAddress = ApexPages.currentPage().getHeaders().get(‘X-Salesforce-SIP’);
X-Salesforce-SIP has the value if there is no caching integration (sandbox, developer edition orgs) or via the secure URL.
58. We have a Time Based Workflow and there is Action scheduled to be executed. If we Deactivate the workflow, Scheduled actions will be removed from queue or not?
Even after deactivation of workflow, its action will be active in queue.
59. How to clear the Time based workflow action queue ?
Two ways to achieve this.
- Make criteria false for all those records.
- Go to Set up -> Monitoring -> Time Based Workflow and search for scheduled actions and then remove from queue.
60. We have Time Based Workflow and there is action scheduled to be executed. Can we delete that workflow?
If a workflow have any pending time dependent action, then we cannot delete the workflow.
While creating workflow on Task object, what difference observed on available actions?
Send Email action is not available while creating workflow on task object.
61. Explain few considerations for @Future annotation in Apex.
Answer :
Remember that any method using the future annotation requires special consideration because the method does not necessarily execute in the same order it is called.
- Methods with the future annotation cannot be used in Visualforce controllers in either getMethodName or setMethodName methods, nor in the constructor.
- You cannot call a method annotated with future from a method that also has the future annotation. Nor can you call a trigger from an annotated method that calls another annotated method.
- Method must be static
- Cannot return anything i.e. ( Only Void )
- Parameter to @future method can only be primitive or collection of primitive data type.
- To test @future methods, you should use startTest and stopTest to make it synchronous inside Test class.
62. How you can use Datetime field as a criteria in SOQL Query ?
Answer :
We cannot use Datetime as condition in Where Clause in between single Quotes.
You can do something like this ,
WHERE CreatedDate > 2017–01–02T00:00:00Z
OR you can also use Date Literals like
WHERE CreatedDate > YESTERDAY
63. Why I am not able to find list of Person Account fields in Field Level Security (FLS) settings when navigated to fields on Account Object.
Answer :
Field Level Security (FLS) of Person Account fields are controlled by Contact Fields. So, if you want to setup FLS of Person Account Fields navigate to fields of Contact and it will be reflected on Person Account.
64. Explain functionality of Force.com Query Optimizer.
Answer :
The Force.com query optimizer:
- Determines the best index from which to drive the query, if possible, based on filters in the query
- Determines the best table to drive the query from if no good index is available
- Determines how to order the remaining tables to minimize cost
- Injects custom foreign key value tables as needed to create efficient join paths
- Influences the execution plan for the remaining joins, including sharing joins, to minimize database input/output (I/O)
- Updates statistics
65.How to report on User License field?
Answer :
Create formula field in User Object with formula Profile.UserLicense.Name.
Note: You need to copy and paste this value because it doesn’t show up in the fields drop down.
66. Explain Skinny table in Salesforce.
Answer :
Salesforce creates skinny tables to contain frequently used fields and to avoid joins, and it keeps the skinny tables in sync with their source tables when the source tables are modified. To enable skinny tables, contact Salesforce.com Customer Support.
For each object table, Salesforce maintains other, separate tables at the database level for standard and custom fields. This separation ordinarily necessitates a join when a query contains both kinds of fields. A skinny table contains both kinds of fields and does not include soft-deleted records.
67. What are the considerations for Skinny Table?
Answer :
- Skinny tables can contain a maximum of 100 columns.
- Skinny tables cannot contain fields from other objects.
- Skinny tables are not copied to sandbox organizations. To have production skinny tables activated in a sandbox organization, contact Salesforce.com Customer Support.
68. How to capture errors after using Database DML methods in Salesforce?
Answer :
List<Contact> lstContact = new List<Contact>();
Contact con = new Contact (lastName = ‘Talekar’, SQL_Server_Id__c=’3′,firstName=’Nitish’);
lstContact.add(con);
// add some other contacts records in contact List
Database.UpsertResult[] results = Database.upsert( lstContact, Contact.SQL_Server_Id__c.getDescribe().getSObjectField() ,false ) ;
for(Integer i=0;i<results.size();i++){
if (!results.get(i).isSuccess()){
Database.Error err = results.get(i).getErrors().get(0);
System.debug(‘Error — ‘+err.getMessage() + ‘\nStatus Code : ‘+err.getStatusCode()+’\n Fields : ‘+err.getFields());
}
}
69. Which fields are automatically Indexed in Salesforce ?
Answer :
- RecordTypeId
- Division
- CreatedDate
- Systemmodstamp (LastModifiedDate)
- Name
- Email (for contacts and leads)
- Foreign key relationships (lookups and master-detail)
- The unique Salesforce record ID, which is the primary key for each object.
70. Which fields cannot be added as a custom Index?
Answer :
- multi-select picklist
- text area (long)
- text area (rich)
- non-deterministic formula fields (Like any formula field using function NOW() or Today() )
- encrypted text fields.
71. What is best practice to refer dynamic custom messages in Visualforce with multi-language support ?
Answer :
Using Custom Label or OutputField or InputField tag, Platform itself will take care of internationalization. However in some cases, Message needs to be dynamic at the same time it should also support muti-language. In Custom Label, we cannot save dynamic String.
Let’s assume we want to show message something like “DEVELOPERNAME is not authorized to access this page”.
Here, Developername should be dynamically changed in visualforce which supports multilanguage. For each developername, it is not feasible to create custom labels. So below workaround can be used :
Step 1 : Create a Custom Label with text {0} is not authorized to access this page. In every language, dynamic value should represented by {0}.
Step 2 : In Controller of Visualforce write something like this :
String developerName = ‘Some Developer Name’;
String message = String.format(Label.DEVELOPERNAME , new String[] { developerName });
72. What are the tools included in lightning ?
Answer :
Lightning Component Framework — Components and extensions that allow you to build reusable components, customise the Salesforce1 Mobile App, and build standalone apps.
Lightning App Builder — A new UI tool that lets you build apps lightning fast, using components provided by Salesforce and platform developers.
Lightning Connect — An integration tool that makes it easier for your Force.com app to consume data from any external source that conforms to the OData spec.
Lightning Process Builder — A UI tool for visualizing and creating automated business processes.
Lightning Schema Builder — A UI tool for viewing and creating objects, fields, and relationships.
73. Difference between Chatter API and Connect API in Salesforce.
Chatter API is REST API for Chatter to display Salesforce data, especially in mobile applications. Responses are localized, structured for presentation, and can be filtered to contain only what the app needs.
Connect API provides apex classes for accessing the same data available in Chatter REST API. Use Chatter in Apex to create custom Chatter experiences in Salesforce.
74. What the Concurrent Request Limit is and Why it Exists in Salesforce?
The multi tenant Force.com platform uses governor limits to ensure that system resources are available to all customers and to prevent any one customer from monopolizing them. If a governor limit is exceeded, the associated execution governor limit issues a runtime exception that cannot be handled. When you design your applications, you can help plan for their growth by keeping these limits in mind.
One of the limits customers frequently reach is the concurrent request limit. Once a synchronous Apex request runs longer than 5 seconds, it begins counting against this limit. Each organisation is allowed 10 concurrent long-running requests. If the limit is reached, any new synchronous Apex request results in a runtime exception. This behavior occurs until the organization’s requests are below the limit.
Ultimately, this limit is in place to protect the user experience. Once the limit is reached, new synchronous Apex requests are denied. This behaviour can be disruptive to your work.
Some useful tips:
- Convert synchronous processes to asynchronous processes. Batch Apex might be a viable alternative. Limit synchronous Web service callout.
- Use the Streaming API instead of polling
- Tune SOQL and DML operations. Make sure that your queries are selective. Limit the number of records in your list views. Avoid data skew.
75: What is custom metadata type ?
Answer : Custom metadata is customizable, deployable, packageable, and upgradeable application metadata. First, you create a custom metadata type, which defines the form of the application metadata. Then you build reusable functionality that determines the behavior based on metadata of that type. Similar to a custom object or custom setting, a custom metadata type has a list of custom fields that represent aspects of the metadata.
Before Custom metadata type, we were using Custom settings of List type. Problem with custom setting was that, during migration or in packages, data were not migrated. We had to either use data loader or some API to create initial data. However, if we package custom metadata type or migrate it, data will also be migrated along with it.
76: Which component in Salesforce ends with __mdt and __s ?
Answer : Custom metadata types ends with __mdt (meta data type), just like custom object or custom fields ends with __c.
When we create Geolocation field in Salesforce, lets say by name location__cthen internally Salesforce creates subfields with extension __s.
In this case location_latitude__s and location_longitude__s.
77: Which interface needs to be implemented in Apex to be used in Flow ?
Answer : We can execute apex as well using flow by annotating it with @InvocableMethod and marking method as static. However this method only takes one parameter of type list. If we want to send multiple parameters, then simplest way is to create comma separated list of argument and pass it. In this method, we can break it and use according.
Below is sample code
Global class Flow_UpdateContactField {
@InvocableMethod
public static void performUpdate(List<String> lstCSV){
List<String> recIds = lstCSV[0].split(‘,’);
// 0 — ContactId, 1-field1__c
Contact objCon = new Contact(Id=recIds[0], field1__c=recIds[1]);
update objCon;
}
}
78: How to get the list of all available sobject in salesforce database using Apex (Dynamic Apex) ?
Answer :
Map<String, Schema.SObjectType> m = Schema.getGlobalDescribe();
79. How to display error messages in the visualforce page ?
Answer :
In Apex use below code to create the error message for visualforce.
Apexpages.addMessage( new ApexPages.Message (ApexPages.Severity.ERROR, ‘Required fields are missing. ‘));
And in Visualforce page, add below tag where you want to display the error message which display the error message.
<apex:pageMessages > </apex:pageMessages>
80: How to read the parameter value from the URL in Apex?
Answer :
Consider that the parameter name is AccountName then use below code snippet:
String objAccountName = Apexpages.currentPage().getParameters().get(‘AccountName’);
81. How to get the debug log of Connection user in salesforce to salesforce Integration?
Answer :
When configuring Debug Logs, you cannot choose a Salesforce to Salesforce Connection User from the User Lookup, but there is a workaround to achieve this.
To begin capturing Debug Logs for a Connection User open the following URL in your browser:
https://YOURSALESFORCEINSTANCE.salesforce.com/p/setup/layout/AddApexDebugLogUser?retURL=%2Fsetup%2Fui%2FlistApexTraces.apexp&UserLookupInput_lkid=YYYYYYYYYYYYYY
&UserLookupInput=Connection%20User
Replace YOURSALESFORCEINSTANCE with your salesforce instance, UserLookupInput_lkid is the ID of the Connection User and UserLookupInput is the User name. You can find the user ID of the connection user, by inspecting the CreatedById for a record created by this user. (eg. via eclipse or Force.com explorer)
82. What are different user licenses available in salesforce and explain them?
Answer : Below is the list of licenses available in salesforce
1) Salesforce : Full access to salesforce CRM and appExchange
2) Salesforce Platform : Access only to Custom apps but not standard CRM
3) Force.com One App : Designed to access only one custom app with unlimited number of tabs
4) Force.com Knowledge Subscription : Grant user access to Force.com Light app or Force.com enterprise app but no CRM functionality
5) Knowledge Only User :Designed for users who only need access to the Salesforce Knowledge app
6) Chatter Free : User has access to chatter which includes feeds, profiles, files and groups
7) Chatter External : Designed to allow customers in Chatter groups. Customers are users outside of a company’s email domain.
8) Chatter Only : User has access to Groups, feeds, people, profiles and files along with access to view accounts and contacts, modify custom objects and use CRM contents, Ideas.
83. What is the difference between Customer portal and Partner portal?
Answer : Traditionally Partner Portal is part of companies Partner Channel Sales efforts. It is a portal focused more on Sales force automation and the efforts of those partners that sell your products to nurture the leads you pass to them, the leads they enter in themselves and the convert to Opportunity and subsequent sale.
Customer Portal on the other hand is more focused on the Service and Support of one’s Customers.
The feature differences are that Partner Portal exposes the Leads and Opportunity objects whereas the Customer Portal does not. However, only the top tier of Partner licensing (Gold Partner licenses) exposes the Case object whereas this is standard in the Customer Portal.
84. What is a Solution in Salesforce?
Answer :
• An answer to a common question or problem
• Enables Customer Support users get up to speed quickly
• Enables Support teams to answer questions quickly and consistently
• Customers search for and browse published Solutions to self assist
• Content-Rich Solutions are an enhancement to the Solution Object which allows solution writers to integrate rich text and
images into their solutions to completely solve a problem
85. Explain Lead conversion?
Answer :
Lead can be converted in salesforce.com and the converted information is mapped to the appropriate business objects — Account, Contact or Opportunity
• The system automatically maps standard lead fields to standard account, contact, and opportunity fields
• For custom lead fields, your administrator can specify how they map to custom account, contact, and opportunity fields
• The system assigns the default picklist values for the account, contact, and opportunity when mapping any standard lead picklist fields that are blank. If your organization uses record types, blank values are replaced with the default picklist values of the new record owner.
• If the lead has a record type, the default record type of the new owner is assigned to records created during lead conversion.
86. Explain the lead conversion process in salesforce?
Answer : When you convert a lead, the standard lead fields are automatically converted to the new account, contact, and, optionally, an opportunity using the information from the lead.
Custom lead fields are converted to custom account, contact, and opportunity fields as specified by your administrator.
All open and closed activities from the lead are attached to the account, contact, and opportunity.
87. What are differences between workflows and approval process?
Answer :
The key difference between workflows and approval process are as below
Workflow rules consist of single step and a single action where as approval process has multiple steps and different actions.
Workflow rules trigger automatically and the rules when triggered are not visible to the user. Approval process on the other hand, contains multiple step s each requiring a specific “I Approve or Reject” user action by the specified approvers.
88. Tell me about Jump Start Wizard versus Standard Wizard in Salesforce?
Answer :
The Jump Start wizard creates a one-step approval process for you in just a few minutes
The Standard Wizard is useful for complex approval processes.
Jump Start Wizard
• The jump start wizard is useful for simple approval processes with a single step.
• Use the jump start wizard if you want to create an approval process quickly by allowing Salesforce to automatically choose some default options for you.
Standard Wizard
• The standard wizard is useful for complex approval processes.
• Use it when you want to fine tune the steps in your approval process.
• The standard wizard consists of a setup wizard that allows you to define your process and another setup wizard that allows you to define each step in the process.
89. What is the Parallel Approval Routing ?
Answer :
Parallel Approval Routing is sending approval requests to multiple approvers in a single step Wait for approval from all the approvers or wait for approval from any one
Configure an approval step to request approval from any combination of multiple users and related users
Configure 25 parallel approvers at each step.
90. What are the Time-Dependent Workflow — Considerations ?
Answer :
Maximum of 10 time triggers per rule
Maximum of 40 actions (10 x 4 types) per time trigger, and 80 actions per workflow rule
Workflow default user must be set up before creating time-based rules
Precision limited to hours or days
Cannot convert leads with time-dependent actions in the Workflow Queue
Time triggers cannot be added to or removed from activated workflow rules
Not possible to create a time-dependent action associated to a rule with a trigger type of Every time the record is created or updated
91. What are the Time-Dependent Workflow Limitations ?
Answer :
Time triggers don’t support minutes or seconds.
Time triggers can’t reference the following:
• DATE or DATETIME fields containing automatically derived functions, such as TODAY or NOW.
• Formula fields that include related-object merge fields.
You can’t add or remove time triggers if:
• The workflow rule is active.
• The workflow rule is deactivated but has pending actions in the queue.
• The workflow rule evaluation criteria are set to Evaluate the rule when a record is: created, and every time it’s edited.
• The workflow rule is included in a package
92. We have a Time Based Workflow and there is Action scheduled to be executed. If we Deactivate the workflow, Scheduled actions will be removed from queue or not?
Answer :
Even after deactivation of workflow, its action will be active in queue.
93. We have Time Based Workflow and there is action scheduled to be executed. Can we delete that workflow?
Answer : If a workflow has any pending time dependent action, then we cannot delete the workflow.
94. How to clear the Time based workflow action queue?
Answer :
Two ways to achieve this:
1. Make criteria false for all those records.
2. Navigate to Set up -> Monitoring -> Time Based Workflow, search for scheduled actions and remove from queue.
95. When the Add Time Trigger button is unavailable?
Answer :
The evaluation criteria are set to Evaluate the rule when a record is: created, and every time it’s edited.
The rule is activated.
The rule is deactivated but has pending actions in the workflow queue.
96. In salesforce which fields are indexed automatically?
Answer :
The following fields are indexed by default:
• primary keys (Id, Name and Owner fields),
• foreign keys (lookup or master-detail relationship fields),
• audit dates (such as LastModifiedDate),
• Custom fields marked as External ID or Unique
97. What is a Category in Salesforce ?
Answer :
• Mechanism to organise Solutions
• Solutions may be associated to one or more Categories
• Categories make up a Solution Category tree structure
What are Suggested Solutions?
• The suggested solutions feature displays up to ten relevant solutions that may help users and customers solve a particular case from the case detail page and the Self-Service portal.
• Suggested Solutions can be enabled for the following:
Cases tab
Self Service Portal
Case auto-response rules and emails.
98. What are different Organization Wide Defaults? Explain each of them?
Answer :
Below are the different OWD values :
Private :
If the OWD for an object is set to private, then only the owner, and users above that role in role hierarchy, can view, edit and report on those records
Public Read Only :
If the OWD for an object is set to Public Read Only, then all users can view and report on records but they cannot edit them. Only the record owner and the users above that role in the role hierarchy can edit the records
Public Read/Write :
If the OWD for an object is set to Public Read/Write, then all users can view, edit and report on all records. But only owner of the record can delete the records.
Public Read/Write/Transfer :
This is available only for Case and Lead objects
If the OWD for an object is set to Public Read/Write/Transfer then, all users can view, edit, Transfer and report on all the records but only owner of the record can delete the records
Public Full Access :
This is available only for Campaign object.
If the OWD for Campaigns are set Public Full Access then, all users can view, edit, delete and report on all records.
No Access, View Only or Use :
This is available only for Price Book object.
If the OWD for Price Book is set Use then, all users can access the Price Book information and as well as using the Price Book configuration for Opportunities with Products.
If the OWD for Price Book is set View Only then, all users can access the Price Book information but not to use that Price Book detail in Opportunities with Products
If the OWD for Price Book is set No Access then, it restricts users from accessing information for Price Book and Prices.
Controlled By Parent :
If the OWD for any object is set as Controlled By Parent, then user can perform an action on the record based on whether they can do the same on the parent record associated with it.
99. What are differences between custom settings and custom objects?
Answer :
Custom Settings:
1. Custom settings are SOQL inexpensive
2. We can’t write triggers on custom settings
3. Fields on which we can create custom settings are restricted like picklists, lookups and formula fields can’t be created in custom settings
4. No Page layouts, record types, validation rules and workflow rules can be used on custom settings.
5. Custom Settings SOQL is faster than custom objects.
Custom Objects:
1. Custom Objects are SOQL Expensive
2. We can have triggers on custom objects
3. No restrictions on creation of fields
4. Can be used on Custom objects
5. Custom objects SOQL not fast as a custom Settings .
100. How to get all the required fields of sObject dynamically?
Answer :
There is no direct property available in Apex dynamic API to represent the required field. However there is another way to know about it.
If any fields have below three properties then it is mandatory field.
1. If it is Creatable
2. If it is not nillable and
3. If it does not have any default value
Map<String, Schema.SObjectType> m = Schema.getGlobalDescribe() ;
Schema.SObjectType s = m.get(so.apiName) ; // Like Account object
Schema.DescribeSObjectResult r = s.getDescribe() ;
Map<String,Schema.SObjectField> fields = r.fields.getMap() ;
for(String f : fields.keyset())
{
Schema.DescribeFieldResult desribeResult = fields.get(f).getDescribe();
if( desribeResult.isCreateable() && !desribeResult.isNillable() && !desribeResult.isDefaultedOnCreate() )
{
//This is mandatory / required field
}
}
101. What is the difference between public cloud & private cloud in salesforce? Is salesforce.com a public cloud or private cloud?
Answer :
Public Cloud: Could services are provided “as a service” over the Internet with little or no control over the underlying technology infrastructure. More than one tenant can use the same resources.
Private Cloud: This also offers activities and functions “as a service” but is deployed over a company intranet or hosted data center. This is private product for a company or organization offering advance security.
Salesforce.com: Is a public cloud as it is hosted on salesforce.com data centers and data of more than one tenant resides on same servers.
102. What is the difference between apex:pageMessages, apex:pageMessage, apex:Message and apex:Messages?
Answer :
apex:PageMessages:
This component displays all messages that were generated for all components on the current page, presented using the salesforce styling. This will display both salesforce generated messages as well as custom messages added to the ApexPages class
apex:PageMessage:
Apex:PageMessage is a component that adds single message on the page. This is used to display custom message using the salesforce formatting
apex:Message:
apex:Message is used to display an error on only a specific field. It is used to allow developers to place field specific errors in specific location.
apex:Messages:
apex:Messages is similar to apex:Message but it displays all errors
103. What are the aggregate functions supported by salesforce SOQL?
Answer :
Following aggregate functions are supported by salesforce SOQL
1. SUM()
2. MIN()
3. MAX()
4. COUNT()
5. AVG()
6. COUNT_DISTINCT()
104. Write a sample aggregate query or explain how to write a aggregate queries?
Answer :
The return types of Aggregate functions are always an array of AggregateResult.
Sample Code
AggregateResult[] ar = [select AVG(Amount) aver from Opportunity];
Object avgAmt = ar[0].get(‘aver’);
105. Write a code to find the average Amount for all your opportunities by campaign?
Answer :
AggregateResult[] arList = [select CampaignId, AVG(amount) from Opportunity group by CampaignId];
for(AggregateResult ar : arList){
System.debug(‘CampaignId ‘ + ar.get(‘CampaignId’));
System.debug(‘Average Amount’ + ar.get(‘expr0’));
}
106. What are groups in SFDC and what is their use in salesforce?
Answer :
Groups are set of users. They can contain individual users, other groups, the users in a particular role or territory, or the users in a particular role or territory plus all of the users below that role or territory in the hierarchy.
There are two types of groups:
• Public groups: Only administrators can create public groups. They can be used by everyone in the organization.
• Personal groups: Each user can create groups for their personal use.
You can use groups in the following ways:
• To set up default sharing access via a sharing rule
• To share your records with other users
• To specify that you want to synchronize contacts owned by others users
• To add multiple users to a Salesforce CRM Content library
• To assign users to specific actions in Salesforce Knowledge
107. Write a syntax and structure of scheduler class?
Answer :
Sample class
global class ScheduleDemo implements Schedulable{
global void execute(SchedulableContext sc){
BatchClass b = new BatchClass();
database.executeBatch(b);
}
}
108 .How to schedule export or take the backup of salesforce?
Answer :
Step by Step Instruction:
- Click Setup >Data Management > Data Export > Schedule Export.
- Select the desired encoding for your export file. Leaving the default is fine.
- Check the Include in export checkbox if you want to include attachments in the export (optional)
- Leave the default Replace carriage returns with spaces if you want your export files to have spaces instead of carriage returns.
- Select Weekly as the frequency for the exports.
- Choose start and end dates. Set the end date to sometime in the distant future such as 20 years from the begin date.
- Set the time of day for your scheduled export. The export is put in a job queue and the exact time of the export will depend on the amount of activity in the queue.
- You can select the types of data to include in your export. It is best to include all data in your export file. This will make sure all your organizations data is exported.
- Click Save.
Points to Remember:
- Formula and roll-up summary fields are never included in exports.
- Articles are not included from exports.
- The export notification email is sent to the email address on file for the user who created the scheduled export. There is no way to indicate another email address. If as an Administrator you want the email to go to another person, have them grant you login access, login as them and schedule the data export.
- Important:
- Scheduled backup exports of your data are limited to weekly exports.
- You have 48 hours from the time you are notified the backup is available to download the backup file.
- The email notification for backups goes to the email address in Salesforce of the person logged in who schedules the backup.
109. How to import attachments using Data Loader in salesforce?
Answer :
Please follow the instructions below.
1. Create an AttachmentList.csv file with the following column headers:
• ParentId — ID of the record to which the attachment should be associated
• Name — Name of the attachment
• ContentType — Format of the extension (e.g. .xls, .pdf, etc)
• OwnerID — ID for the owner of the attachment
• Body — File path to the Attachment on your local machine (C:\Attachments\YourAttachmentFileName.pdf)
2. Log in to the Data Loader.
3. Select the “Insert” command.
4. In the ‘Select Sforce Object’ step, select the ‘Attachments’ object. This object is not displayed by default hence check the ‘Show all Sforce Objects’ checkbox.
5. Choose the AttachmentList.csv file.
6. In the mapping step, map the following fields:
• Parent ID
• Name
• Owner ID
• Body — Make sure to map the Body column which you created previously with the file extension. This is how you designate the file and location of the attachments to be inserted.
7. Click “OK” to start the upload.
110. What is the difference between custom controller and extension in salesforce?
Answer :
Custom Controller: A custom controller is an Apex class that implements all of the logic for a page without leveraging a standard controller. Use custom controllers when you want your Visualforce page to run entirely in system mode, which does not enforce the permissions and field-level security of the current user.
Controller extension: A controller extension is an Apex class that extends the functionality of a standard or custom controller. Use controller extensions when:
• You want to leverage the built-in functionality of a standard controller but override one or more actions, such as edit, view, save, or delete.
• You want to add new actions.
• You want to build a Visualforce page that respects user permissions. Although a controller extension class executes in system mode, if a controller extension extends a standard controller, the logic from the standard controller does not execute in system mode. Instead, it executes in user mode, in which permissions, field-level security, and sharing rules of the current user apply.
A controller extension is any Apex class containing a constructor that takes a single argument of type ApexPages.StandardController or CustomControllerName, whereCustomControllerName is the name of a custom controller you want to extend.
Note: Although custom controllers and controller extension classes execute in system mode and thereby ignore user permissions and field-level security, you can choose whether they respect a user’s organization-wide defaults, role hierarchy, and sharing rules by using the with sharing keywords in the class definition.
111. Difference between with sharing and without sharing in salesforce ?
Answer :
By default, all Apex executes under the System user, ignoring all CRUD, field-level, and row-level security (that is always executes using the full permissions of the current user).
without sharing:
Enforcing the User’s Permissions, Sharing rules and field-level security should apply to the current user.
For example:
public with sharing class sharingClass {
// your Code here
}
without sharing:
Not enforced the User’s Permissions, Sharing rules and field-level security.
For example:
public without sharing class noSharing {
// your Code here
}
Enforcing the current user’s sharing rules can impact: (with sharing)
SOQL and SOSL queries — A query may return fewer rows than it would operating in system context.
DML operations — An operation may fail because the current user doesn’t have the correct permissions. For example, if the user specifies a foreign key value that exists in the organization, but which the current user does not have access to.
112. What are email services in salesforce and explain how we can use them in code?
Answer :
Email services are automated processes that use apex class to process the contents, headers and attachment of an inbound email.
Sample code
Use Case: create a contact record if the inbound email subject is Create Contact and body contains contact name
global CreateContactFromEmail implements Messaging.InboundEmailHandler{
global Messaging.InboundEmailResult handleInboundEmail(Messaging.InboundEmail email, Messaging.InboundEnvelop envelop){
Messaging.InboundEmailResult res = new Messaging.InboundEmailResult();
String strToCompare = ‘Create Contact’;
If(email.subject.equalsIgnoreCase(strToCompare)){
Contact c = new Contact();
c.LastName = email.plainTextBody();
insert c;
//save text attachments
for(Messaging.InboundEmail.TextAttachment att : email.textAttachments){
Attachment a = new Attachment();
a.Name = att.fileName;
a.Body = att.Blob.valueOf(att.Body);
a.ParentId = c.Id;
insert attachment;
}
//save binary attachments
for (Messaging.Inboundemail.BinaryAttachment bAttachment : email.binaryAttachments) {
Attachment attachment = new Attachment();
attachment.Name = bAttachment.fileName;
attachment.Body = bAttachment.body;
attachment.ParentId = c.Id;
insert attachment;
}
}
res.Success = true;
return res;
}
}
113. What is Wrapper Class in Apex Salesforce ?
Answer :
Wrapper class is collections of different data type, subject etc.
In following example we are bind Account ,Opportunity standard object. We query and perform
business logic on the Collection of elements across unrelated objects with the custom data type.
Visual Force Page:
<apex:page controller=”wrapperDemoCtrl”>
<apex:pageBlock title=”Account From wrapper Class”>
<apex:pageBlockTable value=”{!wraccount}” var=”wra”>
<apex:column value=”{!wra.acc.Name}”/>
</apex:pageBlockTable>
</apex:pageBlock>
<apex:pageBlock title=”Opportunity From wrapper Class”>
<apex:pageBlockTable value=”{!wraoppn}” var=”wropp”>
<apex:column value=”{!wropp.op.Name}”/>
</apex:pageBlockTable>
</apex:pageBlock>
</apex:page>
Apex Controller :
public class wrapperDemoCtrl {
public list<wrapperClass> wraplist{get;set;}
public list<wrapperClass> getwraccount()
{
list<Account>acclist=[select Id,Name from Account limit 3];
wraplist= new list<wrapperClass>();
for(Account acn: acclist)
{
wraplist.add(new wrapperClass(acn));
}
return wraplist;
}
public list<wrapperClass> getwraoppn()
{
list<Opportunity>opplist=[select Id,Name from Opportunity limit 3];
wraplist= new list<wrapperClass>();
for(Opportunity opn:opplist )
{
wraplist.add(new wrapperClass(opn));
}
return wraplist;
}
public class wrapperClass{
public Account acc {get;set;}
public Opportunity op {get;set;}
public wrapperClass(Account accn){
acc= accn;
}
public wrapperClass(Opportunity opn)
{
op=opn;
}
}
}
114. How can we hard delete a record using a Apex class/by code?
Answer :
ALL ROWS key word can be used to get all the records including records in the recycle bin.
Below is the sample code to delete contact records from recycle bin
List<Contact> dContactList=[Select ID From Contact Where IsDeleted = true limit 199 ALL ROWS];
Database.emptyRecycleBin( dContactList );
How do you do File Upload using visualforce?
Answer :
Below is the code sample of file upload in visualforce
<! — Upload a file and put it in your personal documents folder →
<! — Page: →
<apex:page standardController=”Document” extensions=”documentExt”>
<apex:messages />
<apex:form id=”theForm”>
<apex:pageBlock>
<apex:pageBlockSection>
<apex:inputFile value=”{!document.body}” filename=”{!document.name}”/>
<apex:commandButton value=”Save” action=”{!save}”/>
</apex:pageBlockSection>
</apex:pageBlock>
</apex:form>
</apex:page>
/*** Controller ***/
public class documentExt {
public documentExt(ApexPages.StandardController controller) {
Document d = (Document) controller.getRecord();
d.folderid = UserInfo.getUserId(); //this puts it in My Personal Documents
}
}
115. Explain Class Constructors with example?
Answer :
• A constructor is a special method used to create (or instantiate) an object out of a class definition.
• Constructors never have explicit return types.
• Constructors have the same name as the class.
• Classes have default, no-argument, public constructor if no explicit constructors is defined.
• If you create a constructor that takes arguments and still want a no-argument constructor, you must explicitly define one.
• Constructors can be overloaded, meaning you can have multiple constructors with different parameters, unique argument lists, or signatures.
• Constructors are called before all other methods in the class.
For Example:
public class TestObject2 {
private static final Integer DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
Integer size;
//Constructor with no arguments
public TestObject2() {
this(DEFAULT_SIZE); // Using this(…) calls the one argument constructor
}
// Constructor with one argument
public TestObject2(Integer ObjectSize) {
size = ObjectSize;
}
}
New objects of this type can be instantiated with the following code:
TestObject2 myObject1 = new TestObject2(20);
TestObject2 myObject2 = new TestObject2();
116. What are the available Trigger Events?
Answer :
There are 6 trigger events available.
1. Insert
2. Update
3. Delete
4. Merge
5. Upsert
6. Undelete
117. What are the available Trigger contest variables?
Answer :
Below are the list of Trigger context variables
1. isBefore
2. IsAfter
3. isInsert
4. IsUpdate
5. isDelete
6. isUndelete
7. isExecuting
8. new
9. old
10. newMap
11. oldMap
12. size
118. Let’s say we have to update the same record in After Trigger context. Is there any way or workaround?
Answer :
If we create a new instance of a sObject in the Apex Trigger in memory using the Id of the newly created record as provided in the After Trigger context, we can perform an Update DML statement and not get a read only error. This is because in Apex, the SObject is seen as a new reference (even though the records have the same SFDC ID) and therefore is eligible for DML operations. The below snippet of code illustrated this working and not working.
List<Contact> originals = new List<Contact>();
if(mirrorResultMap.values().size() > 0)
{
for(Contact origContact : contactRecs.values())
{
Contact mirrorContact = mirrorResultMap.get(origContact.Id);
//origContact.Linked_Contact__c = mirrorContact.Id; //Link the Original Record i.e. Mirror Record WILL FAIL
Contact origContactUpdate = new Contact(Id=origContact.Id, Linked_Contact__c = mirrorContact.Id); //This will WORK
originals.add(origContactUpdate);
}
//update contactRecs.values(); //Update the Records -> THIS WILL FAIL AS ITS ORIGINAL RECORDS IN MEMORY
update originals;
}
119. How to get the picklist value in Apex class?
Answer :
Using Dynamic apex, we can achieve this. On object of type pickilist, call getDescribe(). Then call the getPicklistValues() method. Iterate over result and create a list. Bind it to <apex:selectOptions>.
Code Example:
Let’s say we have a custom object called OfficeLocation__c. This object contains a picklist field Country__c.
The first thing we need to do, within our controller is use the getDescribe() method to obtain information on
the Country__c field:
Schema.DescribeFieldResult fieldResult = OfficeLocation__c.Country__c.getDEscribe();
We know that Country__c is a picklist, so we want to retrieve the picklist values:
List<Schema.PicklistEntry> ple = fieldResult.gerPicklistValues();
The only thing left for us to do is map the picklist values into an <apex:selectOptions> tag can use for display. Here is the entire method from our controller to do this:
public List<SelectOption> getCountries()
{
List<SelectOption> options = new List<SelectOption>();
Schema.DescribeFieldResult fieldResult =
OfficeLocation__c.Country__c.getDescribe();
List<Schema.PicklistEntry> ple = fieldResult.getPicklistValues();
for( Schema.PicklistEntry f : ple)
{
options.add(new SelectOption(f.getLabel(), f.getValue()));
}
return options;
}
With our controller logic all complete, we can call the getCountries() method from our Visualforce page, and populate the <apex:selectList> tag:
<apex:selectList id=”countries” value=”{!Office_Location__c.Country__c}”
size=”1″ required=”true”>
<apex:selectOptions value=”{!countries}”/>
</apex:selectList>
120. What are the Salesforce annotations ?
Answer :
Apex annotations modify the way a method or class is used.
Below is the list of annotations supported by salesforce :
@Deprecated:
Use the deprecated annotation to identify methods, classes, exceptions, enums, interfaces, or variables that can no longer be referenced in subsequent releases of the managed package in which they reside. This is useful when you are re-factoring code in managed packages as the requirements evolve. New subscribers cannot see the deprecated elements, while the elements continue to function for existing subscribers and API integrations.
@Future:
Use the future annotation to identify methods that are executed asynchronously. When you specify future, the method executes when Salesforce has available resources.
To test methods defined with the future annotation, call the class containing the method in a startTest, stopTest code block. All asynchronous calls made after the startTest method are collected by the system. When stopTest is executed, all asynchronous processes are run synchronously.
@IsTest:
Use the isTest annotation to define classes or individual methods that only contain code used for testing your application. The isTest annotation is similar to creating methods declared as testMethod.
@ReadOnly:
The @ReadOnly annotation allows you to perform unrestricted queries against the Force.com database. All other limits still apply. It’s important to note that this annotation, while removing the limit of the number of returned rows for a request, blocks you from performing the following operations within the request: DML operations, calls to System.schedule, calls to methods annotated with @future, and sending emails.
@RemoteAction:
The RemoteAction annotation provides support for Apex methods used in Visualforce to be called via JavaScript. This process is often referred to as JavaScript remoting.
@TestVisible:
Use the TestVisible annotation to allow test methods to access private or protected members of another class outside the test class. These members include methods, member variables, and inner classes. This annotation enables a more permissive access level for running tests only.
Apex REST annotations:
@RestResource(urlMapping=’/yourUrl’):
The @RestResource annotation is used at the class level and enables you to expose an Apex class as a REST resource.
@HttpDelete:
The @HttpDelete annotation is used at the method level and enables you to expose an Apex method as a REST resource. This method is called when an HTTP DELETE request is sent, and deletes the specified resource.
@HttpGet:
The @HttpGet annotation is used at the method level and enables you to expose an Apex method as a REST resource. This method is called when an HTTP GET request is sent, and returns the specified resource.
@HttpPatch:
The @HttpPatch annotation is used at the method level and enables you to expose an Apex method as a REST resource. This method is called when an HTTP PATCH request is sent, and updates the specified resource.
@HttpPost:
The @HttpPost annotation is used at the method level and enables you to expose an Apex method as a REST resource. This method is called when an HTTP POST request is sent, and creates a new resource.
@HttpPut:
The @HttpPut annotation is used at the method level and enables you to expose an Apex method as a REST resource. This method is called when an HTTP PUT request is sent, and creates or updates the specified resource.
121. What are the Trigger Best Practices ?
Answer :
Best Practice #1: One Trigger Per Object
A single Apex Trigger is all you need for one particular object. If you develop multiple Triggers for a single object, you have no way of controlling the order of execution if those Triggers can run in the same contexts. Many times, the order of execution doesn’t matter but when it does matter, it’s nearly impossible to maintain proper flow control. A single Trigger can handle all possible combinations of Trigger contexts which are:
- before insert
- after insert
- before update
- after update
- before delete
- after delete
- after undelete
So as a best practice, create one Trigger per object and let it handle all of the contexts that you need. Here is an example of a Trigger that implements all possible contexts:
trigger OpportunityTrigger on Opportunity (
before insert, before update, before delete,
after insert, after update, after delete, after undelete) {
// trigger body
}
Best Practice #2: Bulkify your Helper Methods
Make sure any code that runs a query or DML operation does it in a bulk manner and doesn’t execute within an iteration or a for loop. Executing queries or DML operations within an iteration adds risk that the governor limits will be exceeded. This is also true for any helper or utility methods an Apex request executes.
Governor limits are calculated at runtime. After the request is initiated (Trigger, Visualforce page, etc.), any Apex code executed in that transaction applies and shares the governor limits. So if a trigger uses some Apex methods written in a helper class, it’s important that those shared Apex methods are properly designed to handle bulk records. These methods should be written to be invoked with a set of records, especially if the method has a SOQL query or DML operation.
For example, if the Apex method performs a SOQL query, that method should receive a collection (Array, List, Set, etc.) of records so when it performs the query, it can perform the query for all records in the Apex transaction. Otherwise, if the Apex method is called individually for each record being processed, the Apex transaction will inefficiently run queries and possibly exceed the allowed number of queries allowed in that transaction. The same is true for DML statements in Apex methods.
So please make sure any utility or helper methods are efficiently written to handle collections of records. This will avoid unnecessarily executing inefficient queries and DML operations.
Best Practice #3: Logic-less Triggers
Another widely-recognized best practice is to make your Triggers logic-less. That means, the role of the Trigger is just to delegate the logic responsibilities to some other handler class. There are many reasons to do this. For one, testing a Trigger is difficult if all of the application logic is in the trigger itself. If you write methods in your Triggers, those can’t be exposed for test purposes. You also can’t expose logic to be re-used anywhere else in your org.
Good old OO principles tell us that this is a bad practice. And to top it all off, cramming all of your logic into a Trigger is going to make for a mess one day. To remedy this scenario, just create a handler class and let your Trigger delegate to it. Here is an example:
trigger OpportunityTrigger on Opportunity (after insert) {
OpportunityTriggerHandler.handleAfterInsert(Trigger.new);
}
And the handler class:
public class OpportunityTriggerHandler {
public static void handleAfterInsert(List opps) {
// handler logic
}
}
Best Practice #4: Avoid SOQL Queries or DML statements inside FOR Loops
A common mistake is that queries or DML statements are placed inside a for loop. There is a governor limit that enforces a maximum number of SOQL queries. There is another that enforces a maximum number of DML statements (insert, update, delete, undelete). When these operations are placed inside a for loop, database operations are invoked once per iteration of the loop making it very easy to reach these governor limits.
Instead, move any database operations outside of for loops. If you need to query, query once, retrieve all the necessary data in a single query, then iterate over the results. If you need to modify the data, batch up data into a list and invoke your DML once on that list of data.
Best Practice #5: Using Collections, Streamlining Queries, and Efficient For Loops
It is important to use Apex Collections to efficiently query data and store the data in memory. A combination of using collections and streamlining SOQL queries can substantially help writing efficient Apex code and avoid governor limits.
Best Practice #6: Querying Large Data Sets
The total number of records that can be returned by SOQL queries in a request is 50,000. If returning a large set of queries causes you to exceed your heap limit, then a SOQL query for loop must be used instead. It can process multiple batches of records through the use of internal calls to query and queryMore.
For example, if the results are too large, the syntax below causes a runtime exception:
//A runtime exception is thrown if this query returns enough records to exceed your heap limit.
Account[] accts = [SELECT id FROM account];
Instead, use a SOQL query for loop as in one of the following examples:
// Use this format for efficiency if you are executing DML statements
// within the for loop. Be careful not to exceed the 150 DML statement limit.
Account[] accts = new Account[];
for (List<Account> acct : [SELECT id, name FROM account
WHERE name LIKE ‘Acme’]) {
// Your logic here
accts.add(acct);
}
update accts;
Let the Force.com platform chunk your large query results into batches of 200 records by using this syntax where the SOQL query is in the for loop definition, and then handle the individual datasets in the for loop logic.
Best Practice #7: Use of the Limits Apex Methods to Avoid Hitting Governor Limits
Apex has a System class called Limits that lets you output debug messages for each governor limit. There are two versions of every method: the first returns the amount of the resource that has been used in the current context, while the second version contains the word limit and returns the total amount of the resource that is available for that context.
122. What are Apex Unit Tests?
Answer:
To facilitate the development of robust, error-free code, Apex supports the creation and execution of unit tests. Unit tests are class methods that verify whether a particular piece of code is working properly. Unit test methods take no arguments, commit no data to the database, send no emails, and are flagged with the testMethod keyword or the isTest annotation in the method definition. Also, test methods must be defined in test classes, that is, classes annotated with isTest.
For example:
@isTest
private class myClass {
static testMethod void myTest() {
// code_block
}
}
This is the same test class as in the previous example but it defines the test method with the isTest annotation instead.
@isTest
private class myClass {
@isTest static void myTest() {
// code_block
}
}
123. What are the Unit Test Considerations ?
Answer :
Here are some things to note about unit tests.
- Starting with Salesforce API 28.0, test methods can no longer reside in non-test classes and must be part of classes annotated with isTest. See the TestVisible annotation to learn how you can access private class members from a test class.
- Test methods can’t be used to test Web service callouts. Instead, use mock callouts. See Test Web Service Callouts and Testing HTTP Callouts.
- You can’t send email messages from a test method.
- Since test methods don’t commit data created in the test, you don’t have to delete test data upon completion.
- If a test class contains a static member variable, and the variable’s value is changed in a testSetup or test method, the new value isn’t preserved. Other test methods in this class get the original value of the static member variable. This behavior also applies when the static member variable is defined in another class and accessed in test methods.
- For some sObjects that have fields with unique constraints, inserting duplicate sObject records results in an error. For example, inserting CollaborationGroup sObjects with the same names results in an error because CollaborationGroup records must have unique names.
- Tracked changes for a record (FeedTrackedChange records) in Chatter feeds aren’t available when test methods modify the associated record. FeedTrackedChange records require the change to the parent record they’re associated with to be committed to the database before they’re created. Since test methods don’t commit data, they don’t result in the creation of FeedTrackedChange records. Similarly, field history tracking records (such as AccountHistory) can’t be created in test methods because they require other sObject records to be committed first (for example, Account).
124. How do you unit test a trigger when you don’t know the required fields?
Answer :
Customers can have validation on custom fields via validation rules and triggers, so handling that in your unit tests without customer intervention is next to impossible. The first step to reducing issues is to have your test data populate all standard fields and ensure the data uses the most common formatting for your customer base (US style phone numbers and addresses for the US for example).
Beyond that you can use the new Reflection features added to Salesforce in Summer ’12 to allow customers to create unit test data classes that can be used by your managed package. Basically you define a test data generation interface and the customer creates an Apex class to generate data for you. Here’s an example of using Reflection in a similar manner on the DeveloperForce blog:http://blogs.developerforce.com/developer-relations/2012/05/dynamic-apex-class-instantiation-in-summer-12.html
Using the method for unit tests run on install might be problematic as you’d have to have the customer create the class before they install your package and your package could only look for the class by name (or iterate through all default namespace classes and check for the correct interface). However, it’s no longer necessary for unit tests to run during installation for managed packages and by default they do not.
The Reflection method requires some coding knowledge on the customer side, but you could add a tool in your application to generate the custom unit test data class for the customer.
FYI, it’s no longer necessary for managed package unit tests to succeed in customer orgs. They’re not required on install, they will no longer prevent deployment to production and they don’t count as part of the customers unit test coverage percentage for purposes of deployment. The only exception to that is if the customer uses ANT and sets the runAllTests parameter to true.
125. How do you write a unit test for a trigger whose only function is to make a callout?
Answer :
Both future methods and callouts can be unit tested.
To test future methods simply make your call to any future method between Test.startTest();and Test.stopTest(); statements and the future method will return when Test.stopTest(); is called. See the documentation for the Test class here: System.Test
Testing callouts is a bit trickier though. Basically in your callout code you check to see if you’re executing within a unit test context by checking Test.isRunningTest() and instead of getting your callout response from an HttpResponse.send() request, you return a pre-built test string instead. There’s one example of this method here: http://www.iterativelogic.com/unit-test-callouts-in-apex-code-part-2/
There’s also an older example of callout unit testing that uses a static variable you set in your unit test. Just replace that static variable with a call to Test.isRunningTest() and their example works fairly well as well. That example can be found here:http://sfdc.arrowpointe.com/2009/05/01/testing-http-callouts/
126. Can I find out if the current user has access to a record without querying?
Answer :
To find out if a particular user has Edit access to a record, use the UserRecordAccess object. This object is available in API version 24.0 and later. You can use SOQL to query this object to find out if the user has edit access to the record in question.
SELECT RecordId, HasEditAccess FROM UserRecordAccess WHERE UserId = [single ID] AND RecordId = [single ID]
If you want to check a batch of records you can use
SELECT RecordId FROM UserRecordAccess WHERE UserId=:UserInfo.getUserId() AND HasReadAccess = true ANDRecordId IN :allRecordIds LIMIT 200
But make sure that allRecordIds is a LIST of IDs. It doesn’t work if allRecordIds is a SET of IDs. I guess that’s a bug.
Also, only a maximum amount of 200 recordIds can be checked in one query.
What is Apex?
Apex is a strongly typed, object-oriented programming language that allows developers to extend the Salesforce platform by writing their own business logic into the platform. Apex looks similar to Java and can be launched through a variety of user-initiated events such as record updates, button clicks, triggers on objects, or external web service requests.
Can you customise Apex & Visualforce directly in a production org?
Apex cannot be customised in a production Org, it must be changed and deployed through a sandbox and meet test coverage. Visualforce, on the other hand, may be customised directly in production (Although this is not best practice)
What are the two options for when Apex Triggers can run?
Apex Triggers can either run before a record has been saved of after. A before operation is usually used to verify information that is going to be inserted, and after trigger is used to access data that has previously been entered by a user or system.
When should Apex be used over Workflow rules or Process Builder?
There are various reasons why you should use Apex over declarative automation options:
- Workflow rules and Process Builder operations sometimes have feature limitations that can be overcome with Apex. For example, pulling information from an external system.
- When dealing with certain or large sets of data, Apex can be more efficient than declarative options due to less limitations.
What are Governor Limits? Can you name 3 examples?
Salesforce runs on a multitenant environment which means resources (Storage, CPU, Memory) are shared with other companies on the Salesforce platform. This means limits must be in place to ensure that all companies using the Salesforce architecture abide by certain rules and don’t let their code or processes monopolize shared resources. A few examples of Governor Limits are:
- Total number of records retrieved by a SOQL query — 50,000
- Total number of SOQL queries issued — 100 (Synchronous) 200 (Asynchronous)
- Total number of DML statements issued — 150
- Total number of callouts (HTTP requests or Web services calls) in a transaction — 100
- Maximum CPU time on the Salesforce servers — 10,000ms (Synchronous) 60,000ms (Asynchronous)
What is Apex test coverage? What’s the minimum test coverage required to deploy?
To ensure that your code meets certain standards, Apex Code coverage shows you how many executable lines of code in your classes and triggers have been exercised by test methods. Code coverage percentage is a calculation of the number of covered lines divided by the sum of the number of covered lines and uncovered lines. The minimum test coverage required to deploy to production is 75%
What are some Apex best practices?
- Bulkify your code
- Avoid SOQL Queries or DML statements inside FOR Loops
- Avoid Hardcoding IDs
- Use of the Limits Apex Methods to Avoid Hitting Governor Limits
- Querying Large Data Sets
- See full list…
What is an Apex Email Service?
You can use email services to process the contents, headers, and attachments of inbound emails. For example, you can create an email service that automatically creates contact records based on contact information in messages. Read more…
What are the different type of Collections you can have in Apex?
There are three main types of collections…
- Lists — A list is an ordered collection of elements that are distinguished by their indices. List elements can be of any data type — primitive types, collections, sObjects, user-defined types, and built-in Apex types.
- Sets — A set is an unordered collection of elements that do not contain any duplicates. Set elements can be of any data type — primitive types, collections, sObjects, user-defined types, and built-in Apex types.
- Maps — A map is a collection of key-value pairs where each unique key maps to a single value. Keys and values can be any data type — primitive types, collections, sObjects, user-defined types, and built-in Apex types.